来源:中华人民共和国国务院新闻办公室 整理:福建厦门启航翻译有限公司
国务院新闻办公室6月7日发布《抗击新冠肺炎疫情的中国行动》白皮书。全文如下:
抗击新冠肺炎疫情的中国行动
(2020年6月)
中华人民共和国国务院新闻办公室
Fighting Covid-19
China in Action
The State Council Information Office of the People's Republic of China
June 2020

目录
前言
一、中国抗击疫情的艰辛历程
(一)第一阶段:迅即应对突发疫情
(二)第二阶段:初步遏制疫情蔓延势头
(三)第三阶段:本土新增病例数逐步下降至个位数
(四)第四阶段:取得武汉保卫战、湖北保卫战决定性成果
(五)第五阶段:全国疫情防控进入常态化
二、防控和救治两个战场协同作战
(一)建立统一高效的指挥体系
(二)构建全民参与严密防控体系
(三)全力救治患者、拯救生命
(四)依法及时公开透明发布疫情信息
(五)充分发挥科技支撑作用
三、凝聚抗击疫情的强大力量
(一)人的生命高于一切
(二)举全国之力抗击疫情
(三)平衡疫情防控与经济社会民生
(四)14亿中国人民坚韧奉献守望相助
四、共同构建人类卫生健康共同体
(一)中国感谢和铭记国际社会宝贵支持和帮助
(二)中国积极开展国际交流合作
(三)国际社会团结合作共同抗疫
结束语
Contents
Foreword
I.China’s Fight against the Epidemic: A Test of Fire
Stage I: Swift Response to the Public Health Emergency
(December 27, 2019-January 19, 2020)
Stage II: Initial Progress in Containing the Virus
(January 20-February 20, 2020)
Stage III: Newly Confirmed Domestic Cases on the Chinese Mainland Drop to Single Digits
(February 21-March 17, 2020)
Stage IV: Wuhan and Hubei – An Initial Victory in a Critical Battle
(March 18-April 28, 2020)
Stage V: Ongoing Prevention and Control
(Since April 29, 2020)
II.Well-Coordinated Prevention, Control and Treatment
1.Centralized and Efficient Command
2. A Tight Prevention and Control System Involving All Sectors of Society
3.An All-Out Effort to Treat Patients and Save Lives
4. China Has Released Information in an Open and Transparent Manner as Required by Law
5.Science and Technology Underpin China’s Efforts
III.Assembling a Powerful Force to Beat the Virus
1.Lives Are Precious
2.Mobilizing the Whole Country to Fight the Epidemic
3. Coordinating Prevention and Control with Social and Economic Development
4.Uniting as One – China’s Billion People
IV.Building a Global Community of Health for All
1. China Appreciates Support from the International Community
2. China Conducts Active International Exchanges and Cooperation
3. International Solidarity and Cooperation in Fighting the Pandemic
Afterword
前言
Foreword
新型冠状病毒肺炎是近百年来人类遭遇的影响范围最广的全球性大流行病,对全世界是一次严重危机和严峻考验。人类生命安全和健康面临重大威胁。
The Covid-19 global pandemic is the most extensive to afflict humanity in a century. A serious crisis for the entire world, and a daunting challenge, it poses a grave threat to human life and health.
这是一场全人类与病毒的战争。面对前所未知、突如其来、来势汹汹的疫情天灾,中国果断打响疫情防控阻击战。中国把人民生命安全和身体健康放在第一位,以坚定果敢的勇气和决心,采取最全面最严格最彻底的防控措施,有效阻断病毒传播链条。14亿中国人民坚韧奉献、团结协作,构筑起同心战疫的坚固防线,彰显了人民的伟大力量。
This is a war that humanity has to fight and win. Facing this unknown, unexpected, and devastating disease, China launched a resolute battle to prevent and control its spread. Making people’s lives and health its first priority, China adopted extensive, stringent, and thorough containment measures, and has for now succeeded in cutting all channels for the transmission of the virus. 1.4 billion Chinese people have exhibited enormous tenacity and solidarity in erecting a defensive rampart that demonstrates their power in the face of such natural disasters.
中国始终秉持人类命运共同体理念,肩负大国担当,同其他国家并肩作战、共克时艰。中国本着依法、公开、透明、负责任态度,第一时间向国际社会通报疫情信息,毫无保留同各方分享防控和救治经验。中国对疫情给各国人民带来的苦难感同身受,尽己所能向国际社会提供人道主义援助,支持全球抗击疫情。
Having forged the idea that the world is a global community of shared future, and believing that it must act as a responsible member, China has fought shoulder to shoulder with the rest of the world. In an open, transparent, and responsible manner and in accordance with the law, China gave timely notification to the international community of the onset of a new coronavirus, and shared without reserve its experience in containing the spread of the virus and treating the infected. China has great empathy with victims all over the world, and has done all it can to provide humanitarian aid in support of the international community’s endeavors to stem the pandemic.
当前,疫情在全球持续蔓延。中国为被病毒夺去生命和在抗击疫情中牺牲的人们深感痛惜,向争分夺秒抢救生命、遏制疫情的人们深表敬意,向不幸感染病毒、正在进行治疗的人们表达祝愿。中国坚信,国际社会同舟共济、守望相助,就一定能够战胜疫情,走出人类历史上这段艰难时刻,迎来人类发展更加美好的明天。
The virus is currently wreaking havoc throughout the world. China grieves for those who have been killed and those who have sacrificed their lives in the fight, extends the greatest respect to those who are struggling to save lives, and offers true moral support to those who are infected and receiving treatment. China firmly believes that as long as all countries unite and cooperate to mount a collective response, the international community will succeed in overcoming the pandemic, and will emerge from this dark moment in human history into a brighter future.
为记录中国人民抗击疫情的伟大历程,与国际社会分享中国抗疫的经验做法,阐明全球抗疫的中国理念、中国主张,中国政府特发布此白皮书。
To keep a record of China’s efforts in its own fight against the virus, to share its experience with the rest of the world, and to clarify its ideas on the global battle, the Chinese government now releases this white paper.
一、中国抗击疫情的艰辛历程
I. China’s Fight against the Epidemic: A Test of Fire
新冠肺炎疫情是新中国成立以来发生的传播速度最快、感染范围最广、防控难度最大的一次重大突发公共卫生事件,对中国是一次危机,也是一次大考。中国共产党和中国政府高度重视、迅速行动,习近平总书记亲自指挥、亲自部署,统揽全局、果断决策,为中国人民抗击疫情坚定了信心、凝聚了力量、指明了方向。在中国共产党领导下,全国上下贯彻“坚定信心、同舟共济、科学防治、精准施策”总要求,打响抗击疫情的人民战争、总体战、阻击战。经过艰苦卓绝的努力,中国付出巨大代价和牺牲,有力扭转了疫情局势,用一个多月的时间初步遏制了疫情蔓延势头,用两个月左右的时间将本土每日新增病例控制在个位数以内,用3个月左右的时间取得了武汉保卫战、湖北保卫战的决定性成果,疫情防控阻击战取得重大战略成果,维护了人民生命安全和身体健康,为维护地区和世界公共卫生安全作出了重要贡献。
The Covid-19 epidemic is a major public health emergency. The virus has spread faster and wider than any other since the founding of the People’s Republic in 1949, and has proven to be the most difficult to contain. It is both a crisis and a major test for China. The Communist Party of China (CPC) and the Chinese government have addressed the epidemic as a top priority, and taken swift action. General Secretary Xi Jinping has taken personal command, planned the response, overseen the general situation and acted decisively, pointing the way forward in the fight against the epidemic. This has bolstered the Chinese people’s confidence and rallied their strength. Under the leadership of the CPC, the whole nation has followed the general principle of “remaining confident, coming together in solidarity, adopting a science-based approach, and taking targeted measures”, and waged an all-out people’s war on the virus. Through painstaking efforts and tremendous sacrifice, and having paid a heavy price, China has succeeded in turning the situation around. In little more than a single month, the rising spread of the virus was contained; in around two months, the daily increase in domestic coronavirus cases had fallen to single digits; and in approximately three months, a decisive victory was secured in the battle to defend Hubei Province and its capital city of Wuhan. With these strategic achievements, China has protected its people’s lives, safety and health, and made a significant contribution to safeguarding regional and global public health.
截至2020年5月31日24时,31个省、自治区、直辖市和新疆生产建设兵团累计报告确诊病例83017例,累计治愈出院病例78307例,累计死亡病例4634例,治愈率94.3%,病亡率5.6%(见图1、2、3、4)。
As of 24:00 of May 31, 2020, a cumulative total of 83,017 confirmed cases had been reported on the Chinese mainland, 78,307 infected had been cured and discharged from hospital, and 4,634 people had died. This demonstrates a cure rate of 94.3 percent and a fatality rate of 5.6 percent (see charts 1, 2, 3 and 4).
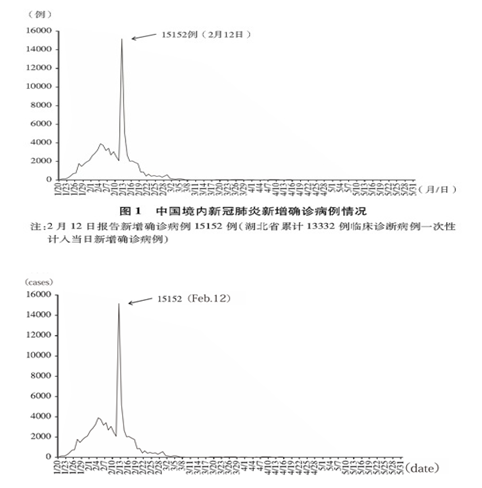
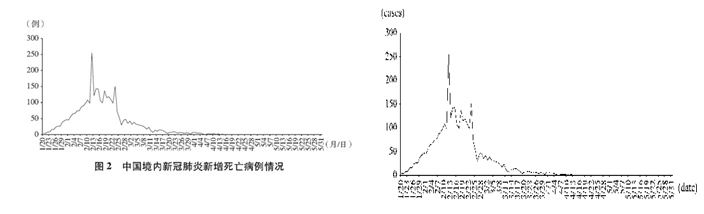
Chart 2. Daily Figure for New Fatalities on the Chinese Mainland
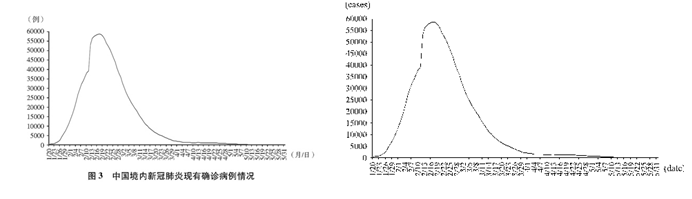
Chart 3. Cumulative Total of Outstanding Cases on the Chinese Mainland
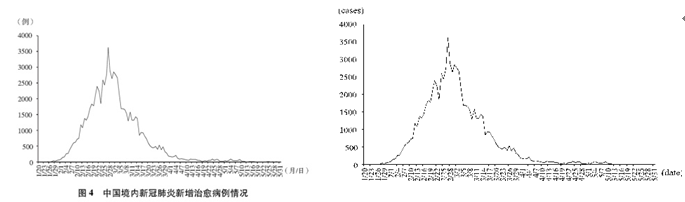
Chart 4. Daily Figure for Cured Cases on the Chinese Mainland
回顾前一阶段中国抗疫历程,大体分为五个阶段。
China’s fight against the epidemic can be divided into five stages.
(一)第一阶段:迅即应对突发疫情
(2019年12月27日至2020年1月19日)
Stage I: Swift Response to the Public Health Emergency
(December 27, 2019-January 19, 2020)
湖北省武汉市监测发现不明原因肺炎病例,中国第一时间报告疫情,迅速采取行动,开展病因学和流行病学调查,阻断疫情蔓延。及时主动向世界卫生组织以及美国等国家通报疫情信息,向世界公布新型冠状病毒基因组序列。武汉地区出现局部社区传播和聚集性病例,其他地区开始出现武汉关联确诊病例,中国全面展开疫情防控。
As soon as cases of pneumonia of unknown cause were identified in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China acted immediately to conduct etiological and epidemiological investigations and to stop the spread of the disease, and promptly reported the situation. In a timely manner, China informed the WHO and other countries, including the US, of the developing situation, and released the genome sequence of the novel coronavirus. After community spread and clusters of cases emerged in Wuhan, and confirmed cases were reported in other Chinese regions, which were due to virus carriers traveling from the city, a nationwide program of epidemic prevention and control was launched.
(1)2019年12月27日,湖北省中西医结合医院向武汉市江汉区疾控中心报告不明原因肺炎病例。武汉市组织专家从病情、治疗转归、流行病学调查、实验室初步检测等方面情况分析,认为上述病例系病毒性肺炎。
(1)December 27, 2019: Hubei Provincial Hospital of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine reported cases of pneumonia of unknown cause to the Wuhan Jianghan Center for Disease Prevention and Control. The Wuhan city government arranged for experts to look into these cases through an analysis of the patients’ condition and clinical outcome, the findings of epidemiological investigations, and preliminary laboratory testing results. The conclusion was that they were cases of a viral pneumonia.
(2)12月30日,武汉市卫生健康委向辖区医疗机构发布《关于做好不明原因肺炎救治工作的紧急通知》。国家卫生健康委获悉有关信息后立即组织研究,迅速开展行动。
(2)December 30: The Wuhan City Health Commission (WCHC)issued Urgent Notice on Treatment of Patients with Pneumonia of Unknown Cause. Upon learning of developments, the National Health Commission (NHC) acted immediately to organize research into the disease.
(3)12月31日凌晨,国家卫生健康委作出安排部署,派出工作组、专家组赶赴武汉市,指导做好疫情处置工作,开展现场调查。武汉市卫生健康委在官方网站发布《关于当前我市肺炎疫情的情况通报》,发现27例病例,提示公众尽量避免到封闭、空气不流通的公众场合和人多集中地方,外出可佩戴口罩。当日起,武汉市卫生健康委依法发布疫情信息。
(3) December 31: The NHC made arrangements in the small hours to send a working group and an expert team to Wuhan to guide its response to the situation and conduct on-site investigations. The WCHC website carried its Information Circular on the Pneumonia Cases in Wuhan, confirming 27 cases and urging the public to stay away from enclosed public places with poor ventilation and venues where large crowds gathered. The commission also suggested the use of face masks when going out. From that day on, the WCHC began to release updates on the disease in accordance with the law.
(4)2020年1月1日,国家卫生健康委成立疫情应对处置领导小组。1月2日,国家卫生健康委制定《不明原因的病毒性肺炎防控“三早”方案》;中国疾控中心、中国医学科学院收到湖北省送检的第一批4例病例标本,即开展病原鉴定。
(4) January 1, 2020: The NHC set up a leading group on the disease response. The next day, it formulated Guidelines on Early Detection, Early Diagnosis and Early Quarantine for Prevention and Control of Viral Pneumonia of Unknown Cause. The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (China CDC) and the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS) received the first batch of samples of four cases discovered in Hubei and began the pathogen identification process.
(5)1月3日,武汉市卫生健康委在官方网站发布《关于不明原因的病毒性肺炎情况通报》,共发现44例不明原因的病毒性肺炎病例。国家卫生健康委组织中国疾控中心等4家科研单位对病例样本进行实验室平行检测,进一步开展病原鉴定。国家卫生健康委会同湖北省卫生健康委制定《不明原因的病毒性肺炎诊疗方案(试行)》等9个文件。当日起,中国有关方面定期向世界卫生组织、有关国家和地区组织以及中国港澳台地区及时主动通报疫情信息。
(5)January 3: The WCHC issued Information Circular on Viral Pneumonia of Unknown Cause, reporting a total of 44 cases. Under the direction of the NHC, China CDC and three other institutions carried out parallel laboratory testing of the samples to identify the pathogen. The NHC and the Health Commission of Hubei Province jointly formulated nine documents, including Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Viral Pneumonia of Unknown Cause (for Trial Implementation). From that day on, on a regular basis, China began to update the WHO, relevant countries, and regional organizations, as well as its own regions of Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan, on the development of the disease.
(6)1月4日,中国疾控中心负责人与美国疾控中心负责人通电话,介绍疫情有关情况,双方同意就信息沟通和技术协作保持密切联系。国家卫生健康委会同湖北省卫生健康部门制定《不明原因的病毒性肺炎医疗救治工作手册》。
(6)January 4: The head of China CDC held a telephone conversation with the director of the US CDC, briefing him about the new pneumonia. The two sides agreed to keep in close contact on information sharing and cooperation on technical matters. The NHC and related health departments in Hubei Province produced Treatment Manual for Viral Pneumonia of Unknown Cause.
(7)1月5日,武汉市卫生健康委在官方网站发布《关于不明原因的病毒性肺炎情况通报》,共发现59例不明原因的病毒性肺炎病例,根据实验室检测结果,排除流感、禽流感、腺病毒、传染性非典型性肺炎和中东呼吸综合征等呼吸道病原。中国向世界卫生组织通报疫情信息。世界卫生组织首次就中国武汉出现的不明原因肺炎病例进行通报。
(7)January 5: The WCHC updated information on its website, reporting a total of 59 cases of the viral pneumonia of unknown cause. Laboratory tests ruled out respiratory pathogens as the cause, such as influenza, avian influenza, adenovirus, the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus, and the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus. China sent a situation update to the WHO. The WHO released its first briefing on cases of pneumonia of unknown cause in Wuhan.
(8)1月6日,国家卫生健康委在全国卫生健康工作会议上通报武汉市不明原因肺炎有关情况,要求加强监测、分析和研判,及时做好疫情处置。
(8)January 6: The NHC gave a briefing on cases of pneumonia of unknown cause in Wuhan at a national health conference, calling for greater efforts to monitor, analyze and study them, and prepare for a timely response.
(9)1月7日,中共中央总书记习近平在主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议时,对做好不明原因肺炎疫情防控工作提出要求。
(9)January 7: Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, presided over a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee and issued instructions on the prevention and control of a possible epidemic of the pneumonia of unknown cause in Wuhan.
(10)1月7日,中国疾控中心成功分离新型冠状病毒毒株。
(10)January 7: China CDC succeeded in isolating the first novel coronavirus strain.
(11)1月8日,国家卫生健康委专家评估组初步确认新冠病毒为疫情病原。中美两国疾控中心负责人通电话,讨论双方技术交流合作事宜。
(11)January 8: An expert evaluation team designated by the NHC initially identified a new coronavirus as the cause of the disease. The heads of the China and US CDCs held a telephone discussion on technical exchanges and cooperation.
(12)1月9日,国家卫生健康委专家评估组对外发布武汉市不明原因的病毒性肺炎病原信息,病原体初步判断为新型冠状病毒。中国向世界卫生组织通报疫情信息,将病原学鉴定取得的初步进展分享给世界卫生组织。世界卫生组织网站发布关于中国武汉聚集性肺炎病例的声明,表示在短时间内初步鉴定出新型冠状病毒是一项显著成就。
(12)January 9: The NHC expert evaluation team released information on the pathogen of the viral pneumonia of unknown cause, and made a preliminary judgment that a new coronavirus was the cause. China informed the WHO of developments and the initial progress that had been made in determining the cause of the viral pneumonia. The WHO released on its website a statement regarding a cluster of pneumonia cases in Wuhan, indicating that the preliminary identification of a novel coronavirus in such a short period of time was a notable achievement.
(13)1月10日,中国疾控中心、中国科学院武汉病毒研究所等专业机构初步研发出检测试剂盒,武汉市立即组织对在院收治的所有相关病例进行排查。国家卫生健康委、中国疾控中心负责人分别与世界卫生组织负责人就疫情应对处置工作通话,交流有关信息。
(13)January 10: Research institutions including China CDC and the Wuhan Institute of Virology (WIV) under the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) came up with an initial version of test kits. Wuhan immediately began to test all relevant cases admitted to local hospitals to screen for the new coronavirus.
The heads of the NHC and China CDC held separate telephone conversations with the head of the WHO about China’s response to the disease, and exchanged information.
(14)1月11日起,中国每日向世界卫生组织等通报疫情信息。
(14)January 11: China started to update the WHO and other parties concerned on a daily basis.
(15)1月12日,武汉市卫生健康委在情况通报中首次将“不明原因的病毒性肺炎”更名为“新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎”。中国疾控中心、中国医学科学院、中国科学院武汉病毒研究所作为国家卫生健康委指定机构,向世界卫生组织提交新型冠状病毒基因组序列信息,在全球流感共享数据库(GISAID)发布,全球共享。国家卫生健康委与世界卫生组织分享新冠病毒基因组序列信息。
(15)January 12: The WCHC changed “viral pneumonia of unknown cause” to “pneumonia caused by the novel coronavirus” in an information circular on its website. China CDC, the CAMS and the WIV, as designated agencies of the NHC, submitted to the WHO the genome sequence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), which was published by the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data to be shared globally.
(16)1月13日,国务院总理李克强在主持召开国务院全体会议时,对做好疫情防控提出要求。
(16)January 13: Premier Li Keqiang chaired a State Council meeting and announced requirements for epidemic prevention and control.
(17)1月13日,国家卫生健康委召开会议,部署指导湖北省、武汉市进一步强化管控措施,加强口岸、车站等人员体温监测,减少人群聚集。世界卫生组织官方网站发表关于在泰国发现新冠病毒病例的声明指出,中国共享了基因组测序结果,使更多国家能够快速诊断患者。香港、澳门、台湾考察团赴武汉市考察疫情防控工作。
(17)January 13: The NHC held a meeting to provide guidance to Hubei and Wuhan authorities, advising them to further strengthen management, step up body temperature monitoring at ports and stations, and reduce crowded gatherings. The WHO issued on its website a statement on the discovery of novel coronavirus cases in Thailand, recognizing that China’s sharing of the genome sequence of the virus had enabled more countries to rapidly diagnose cases. An inspection team from Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan visited Wuhan to learn about the prevention and control of the disease.
(18)1月14日,国家卫生健康委召开全国电视电话会议,部署加强湖北省、武汉市疫情防控工作,做好全国疫情防范应对准备工作。会议指出,新冠病毒导致的新发传染病存在很大不确定性,人与人之间的传播能力和传播方式仍需要深入研究,不排除疫情进一步扩散蔓延的可能性。
(18)January 14: The NHC held a national teleconference, specifying arrangements for epidemic prevention and control in Hubei and Wuhan, and for emergency preparations and response across the country. The NHC cautioned that there was great uncertainty about the new disease, and that more research was needed to understand its mode of transmission and the risk of human-to-human transmissibility. Further spread could not be ruled out.
(19)1月15日,国家卫生健康委发布新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎第一版诊疗方案、防控方案。
(19)January 15: The NHC unveiled the first versions of Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia, and Protocol on Prevention and Control of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia.
(20)1月16日,聚合酶链式反应(PCR)诊断试剂优化完成,武汉市对全部69所二级以上医院发热门诊就医和留观治疗的患者进行主动筛查。
(20)January 16: As the optimization of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) diagnostic reagents was completed, Wuhan began to screen all patients treated in fever clinics or under medical observation in the 69 hospitals at or above the level of grade two in the city.
(21)1月17日,国家卫生健康委派出7个督导组赴地方指导疫情防控工作。
(21)January 17: The NHC sent seven inspection teams to different provincial-level health agencies to guide local epidemic prevention and control.
(22)1月18日,国家卫生健康委发布新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎第二版诊疗方案。
(22)January 18: The NHC released the second version of Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia.
(23)1月18日至19日,国家卫生健康委组织国家医疗与防控高级别专家组赶赴武汉市实地考察疫情防控工作。19日深夜,高级别专家组经认真研判,明确新冠病毒出现人传人现象。
(23) January 18 and 19: The NHC assembled a high-level national team of senior medical and disease control experts and sent them to Wuhan to study the local response to the epidemic. In the middle of the night of January 19, after careful examination and deliberation, the team determined that the new coronavirus was spreading between humans.
(二)第二阶段:初步遏制疫情蔓延势头
(1月20日至2月20日)
Stage II: Initial Progress in Containing the Virus
(January 20-February 20, 2020)
全国新增确诊病例快速增加,防控形势异常严峻。中国采取阻断病毒传播的关键一招,坚决果断关闭离汉离鄂通道,武汉保卫战、湖北保卫战全面打响。中共中央成立应对疫情工作领导小组,并向湖北等疫情严重地区派出中央指导组。国务院先后建立联防联控机制、复工复产推进工作机制。全国集中资源和力量驰援湖北省和武汉市。各地启动重大突发公共卫生事件应急响应。最全面最严格最彻底的全国疫情防控正式展开,疫情蔓延势头初步遏制。(图5)
The situation became most pressing with the rapid increase in newly confirmed cases in China. As a crucial step to stem the spread of the virus, the Chinese government took the decisive measure to close outbound traffic from Wuhan. This marked the beginning of an all-out battle to protect Wuhan and Hubei from the epidemic. The CPC Central Committee set up a leading group for novel coronavirus prevention and control and sent the Central Steering Group to Hubei. A joint epidemic prevention and control mechanism and in due course a mechanism to facilitate resumption of work were set up under the State Council. Resources were mobilized nationwide to assist Hubei and Wuhan. Major public health emergency responses were activated across China. The most comprehensive, stringent and thorough epidemic prevention and control campaign was launched nationwide, and initial progress was made in curbing the spread of the virus (see Chart 5).
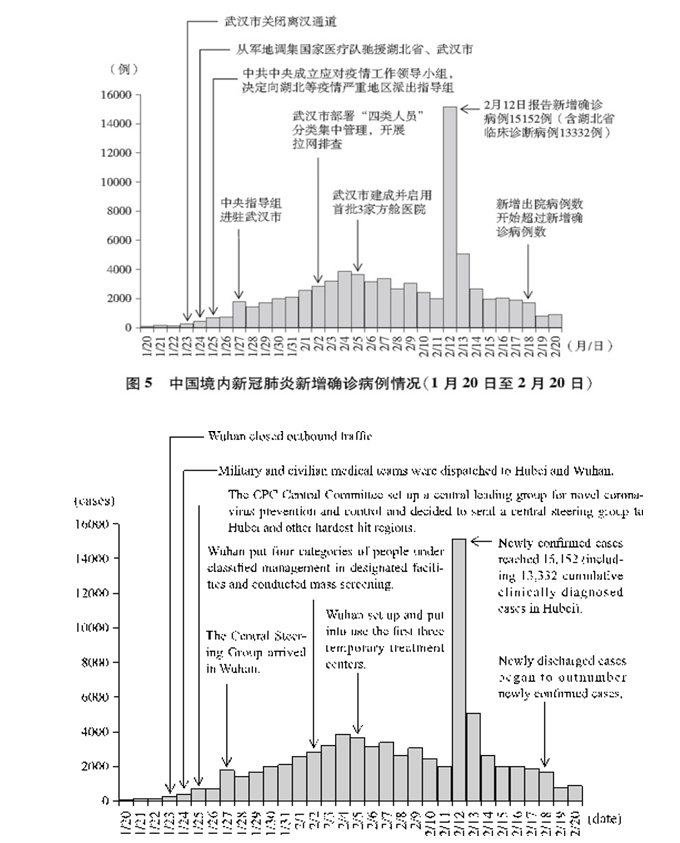
Chart 5. Daily Figure for Newly Confirmed Cases on the Chinese Mainland
(January 20-February 20)
(1)1月20日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席习近平对新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎疫情作出重要指示,指出要把人民生命安全和身体健康放在第一位,坚决遏制疫情蔓延势头;强调要及时发布疫情信息,深化国际合作。
(1)January 20: President Xi Jinping, also general secretary of the CPC Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, gave important instructions on fighting the novel coronavirus. He emphasized that people’s lives and health must come first and resolute efforts should be taken to stem the spread of the virus. He called for prompt release of information on the epidemic and enhanced international cooperation.
(2)1月20日,国务院总理李克强主持召开国务院常务会议,进一步部署疫情防控工作,并根据《中华人民共和国传染病防治法》将新冠肺炎纳入乙类传染病,采取甲类传染病管理措施。
(2)January 20: During an executive meeting of the State Council, Premier Li Keqiang decided to take more steps for epidemic prevention and control. A decision was taken to classify the novel coronavirus pneumonia as a Class B infectious disease in compliance with the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, but to apply to it the preventive and control measures for a Class A infectious disease.
(3)1月20日,国务院联防联控机制召开电视电话会议,部署全国疫情防控工作。
(3)January 20: The State Council convened a teleconference to plan for nationwide prevention and control of the disease.
(4)1月20日,国家卫生健康委组织召开记者会,高级别专家组通报新冠病毒已出现人传人现象。
(4)January 20: The NHC held a press conference for the high-level expert team, at which it was confirmed that the virus could transmit from human to human.
(5)1月20日,国家卫生健康委发布公告,将新冠肺炎纳入传染病防治法规定的乙类传染病并采取甲类传染病的防控措施;将新冠肺炎纳入《中华人民共和国国境卫生检疫法》规定的检疫传染病管理。国家卫生健康委发布《新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎防控方案(第二版)》。
(5)January 20: The NHC made a statement on implementing the above State Council decision and bringing the pneumonia under quarantinable infectious disease management in accordance with the Frontier Health and Quarantine Law of the People’s Republic of China. The NHC also released Protocol on Prevention and Control of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Edition 2).
(6)1月22日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席习近平作出重要指示,要求立即对湖北省、武汉市人员流动和对外通道实行严格封闭的交通管控。
(6)January 22: Xi Jinping ordered the immediate imposition of tight restrictions on the movement of people and channels of exit in Hubei and Wuhan.
(7)1月22日,国家卫生健康委发布《新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎诊疗方案(试行第三版)》。国务院新闻办公室就疫情举行第一场新闻发布会,介绍疫情有关情况。国家卫生健康委收到美方通报,美国国内发现首例确诊病例。国家生物信息中心开发的2019新型冠状病毒信息库正式上线,发布全球新冠病毒基因组和变异分析信息。
(7)January 22: The NHC issued Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Trial Version 3). The State Council Information Office held its first press conference on the novel coronavirus.
The NHC was notified by the United States about its first confirmed case.
The 2019 Novel Coronavirus Resource database was officially launched by the China National Center for Bioinformation, which released the novel coronavirus genome and provided information on variation analysis to the international community.
(8)1月23日凌晨2时许,武汉市疫情防控指挥部发布1号通告,23日10时起机场、火车站离汉通道暂时关闭。交通运输部发出紧急通知,全国暂停进入武汉市道路水路客运班线发班。国家卫生健康委等6部门发布《关于严格预防通过交通工具传播新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎的通知》。1月23日至29日,全国各省份陆续启动重大突发公共卫生事件省级一级应急响应。
(8)January 23: At around 2 a.m. Wuhan City Novel Coronavirus Prevention and Control Command Center issued the No. 1 public notice declaring temporary closure of the city’s outbound routes at its airports and railway stations at 10 a.m. the same day. The Ministry of Transport issued an emergency circular suspending passenger traffic into Wuhan from other parts of the country by road or waterway. The NHC and five other government departments also issued Notice on Preventing the Transmission of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia via Means of Transport. From January 23 to January 29, all provinces and equivalent administrative units on the Chinese mainland (hereafter all provinces) activated Level 1 public health emergency response.
(9)1月23日,中国科学院武汉病毒研究所、武汉市金银潭医院、湖北省疾病预防控制中心研究团队发现新冠病毒的全基因组序列与SARS-CoV的序列一致性有79.5%。国家微生物科学数据中心和国家病原微生物资源库共同建成“新型冠状病毒国家科技资源服务系统”,发布新冠病毒第一张电子显微镜照片和毒株信息。
(9) January 23: Researchers of the WIV, Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital and the Hubei Provincial CDC discovered that the whole genome sequence of the 2019-nCoV shares 79.5 percent of the SARS-CoV sequence. The Novel Coronavirus National Science and Technology Resource Service System, jointly set up by the National Microbiology Data Center and the National Pathogen Resource Collection Center, released the first electron microscope image of the virus and its strain information.
(10)1月24日开始,从各地和军队调集346支国家医疗队、4.26万名医务人员和965名公共卫生人员驰援湖北省和武汉市。
(10)January 24: Dispatch of national medical teams to Hubei and Wuhan began. In the ensuing period, a total of 346 medical teams composed of 42,600 medical workers and 965 public health workers from across the country and the armed forces were dispatched.
(11)1月25日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,明确提出“坚定信心、同舟共济、科学防治、精准施策”总要求,强调坚决打赢疫情防控阻击战;指出湖北省要把疫情防控工作作为当前头等大事,采取更严格的措施,内防扩散、外防输出;强调要按照集中患者、集中专家、集中资源、集中救治“四集中”原则,将重症病例集中到综合力量强的定点医疗机构进行救治,及时收治所有确诊病人。会议决定,中共中央成立应对疫情工作领导小组,在中央政治局常务委员会领导下开展工作;中共中央向湖北等疫情严重地区派出指导组,推动有关地方全面加强防控一线工作。
(11)January 25: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He called for resolute efforts to win the battle to contain the virus with “confidence and solidarity, a science-based approach and targeted measures”. He urged Hubei to make epidemic control its top priority and apply more rigorous measures to stem the spread of the virus within the province and beyond. All confirmed patients, he said, must be hospitalized without delay, and severe cases must be sent to designated hospitals with sufficient medical resources so that they could be treated by medical experts. A decision was taken at the meeting that the central Party leadership would set up a leading group for novel coronavirus prevention and control under the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau. It was also decided that the central Party leadership would send a steering group to Hubei to oversee epidemic control on the ground.
(12)1月25日,国家卫生健康委发布通用、旅游、家庭、公共场所、公共交通工具、居家观察等6个公众预防指南。
(12)January 25: The NHC released six sets of guidelines on disease prevention: for general use, tourism, households, public places, public transport and home observation.
(13)1月26日,中共中央政治局常委、国务院总理、中央应对疫情工作领导小组组长李克强主持召开领导小组第一次全体会议。国务院办公厅印发通知,决定延长2020年春节假期,各地大专院校、中小学、幼儿园推迟开学。国家药监局应急审批通过4家企业4个新型冠状病毒检测产品,进一步扩大新型冠状病毒核酸检测试剂供给能力。
(13)January 26: Premier Li Keqiang, also member of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee and head of the Central Leading Group for Novel Coronavirus Prevention and Control, chaired the group’s first meeting. The General Office of the State Council issued the decision to extend the Chinese New Year holiday of 2020 and postpone the opening of all universities, colleges, secondary schools, elementary schools and kindergartens. The National Medical Products Administration fast-tracked approval of four novel coronavirus test kits made by four companies to boost capacity for producing virus nucleic acid test kits.
(14)1月27日,中共中央总书记习近平作出指示,要求中国共产党各级组织和广大党员、干部,牢记人民利益高于一切,不忘初心、牢记使命,团结带领广大人民群众坚决贯彻落实党中央决策部署,全面贯彻“坚定信心、同舟共济、科学防治、精准施策”的要求,让党旗在防控疫情斗争第一线高高飘扬。
(14)January 27: Xi Jinping issued an instruction calling on all CPC organizations and members to bear in mind the supremacy of the people’s interests and the Party’s founding mission, strengthen confidence and solidarity, take a science-based approach and targeted measures, and lead the people in implementing the decisions made by the central Party leadership.
(15)1月27日,受中共中央总书记习近平委托,中共中央政治局常委、国务院总理、中央应对疫情工作领导小组组长李克强赴武汉市考察指导疫情防控工作,代表中共中央、国务院慰问疫情防控一线的医护人员。同日,中央指导组进驻武汉市,全面加强对一线疫情防控的指导督导。
(15)January 27: Li Keqiang paid an inspection visit to Wuhan on behalf of Xi Jinping, where he gave guidance on virus control and expressed appreciation to frontline health workers. The Central Steering Group arrived in Wuhan on the same day to strengthen overall guidance of and supervision over the prevention and control of the disease at the front line.
(16)1月27日,国家卫生健康委发布《新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎诊疗方案(试行第四版)》。国家卫生健康委负责人应约与美国卫生与公众服务部负责人通话,就当前新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎疫情防控工作进行交流。
(16)January 27: The NHC released Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Trial Version 4).
The head of the NHC discussed epidemic prevention and control with the head of the US Department of Health and Human Services (US HHS) in a telephone call.
(17)1月28日,国家主席习近平在北京会见世界卫生组织总干事谭德塞时指出,疫情是魔鬼,我们不能让魔鬼藏匿;指出中国政府始终本着公开、透明、负责任的态度及时向国内外发布疫情信息,积极回应各方关切,加强与国际社会合作;强调中方愿同世界卫生组织和国际社会一道,共同维护好地区和全球的公共卫生安全。
(17)January 28: Xi Jinping met with WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus in Beijing. He said, “The virus is a devil, and we must hunt it down. The Chinese government has been providing timely updates on the epidemic in an open, transparent and responsible way. We have responded to the concerns of various parties and enhanced cooperation with the international community.” He expressed China’s readiness to work with the WHO and the international community to safeguard public health both in the region and globally.
(18)1月28日,国家卫生健康委发布《新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎防控方案(第三版)》。
(18)January 28: The NHC released Protocol on Prevention and Control of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Edition 3).
(19)1月30日,国家卫生健康委通过官方渠道告知美方,欢迎美国加入世界卫生组织联合专家组。美方当天即回复表示感谢。
(19)January 30: The NHC notified the US through the official channel that American experts were welcome to join the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease. The US replied and expressed its appreciation on the same day.
(20)1月31日,世界卫生组织宣布新冠肺炎疫情构成“国际关注的突发公共卫生事件”。国家卫生健康委发布《新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎重症患者集中救治方案》。
(20)January 31:
The WHO declared the novel coronavirus outbreak a public health emergency of
international concern. The NHC released Guidelines on Treating Novel
Coronavirus Patients with Severe Symptoms in Designated Hospitals.
(21)2月2日开始,在中央指导组指导下,武汉市部署实施确诊患者、疑似患者、发热患者、确诊患者的密切接触者“四类人员”分类集中管理,按照应收尽收、应治尽治、应检尽检、应隔尽隔“四应”要求,持续开展拉网排查、集中收治、清底排查三场攻坚战。
(21)February 2: Under the guidance of the Central Steering Group, Wuhan began to adopt measures to put four categories of people – confirmed cases, suspected cases, febrile patients who might be carriers, and close contacts – under classified management in designated facilities. The policy of ensuring that all those in need are tested, isolated, hospitalized or treated was implemented. Actions were taken to conduct mass screenings to identify people with infections, hospitalize them, and collect accurate data on case numbers.
(22)2月2日,国家卫生健康委负责人致函美国卫生与公众服务部负责人,就双方卫生和疫情防控合作再次交换意见。
(22)February 2: The head of the NHC sent a letter to the head of the US HHS to further exchange views on bilateral cooperation on public health and epidemic prevention and control.
(23)2月3日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,指出要进一步完善和加强防控,严格落实早发现、早报告、早隔离、早治疗“四早”措施;强调要全力以赴救治患者,努力“提高收治率和治愈率”“降低感染率和病亡率”。
(23)February 3: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He required that epidemic control measures be improved and strengthened and that the principle of early detection, reporting, quarantine and treatment be strictly observed. He called for saving lives by raising admission and cure rates and lowering infection and fatality rates.
(24)2月3日,中央指导组从全国调集22支国家紧急医学救援队,在武汉市建设方舱医院。
(24)February 3: The Central Steering Group sent to Wuhan 22 national emergency medical teams from all over China, and gave the order to construct temporary treatment centers.
(25)2月4日,中国疾控中心负责人应约与美国国家过敏症和传染病研究所负责人通电话,交流疫情信息。
(25)February 4: The head of China CDC took a telephone call from the head of the US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases in which they exchanged views on the novel coronavirus.
(26)2月5日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席、中央全面依法治国委员会主任习近平主持召开中央全面依法治国委员会第三次会议,强调要始终把人民生命安全和身体健康放在第一位,从立法、执法、司法、守法各环节发力,全面提高依法防控、依法治理能力,为疫情防控工作提供有力法治保障。
(26)February 5: Xi Jinping chaired the third meeting of the Commission for Law-based Governance under the CPC Central Committee. He stressed the importance of putting the people’s lives and health first, and the need to raise China’s overall capacity of law-based disease prevention and control through the joint efforts of the legislature, law enforcement agencies, the judiciary and the public. This would ensure that epidemic prevention and control is conducted in compliance with the law.
(27)2月5日,国务院联防联控机制加强协调调度,供应湖北省医用N95口罩首次实现供大于需。
(27)February 5: The State Council through its Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism strengthened coordination, which made it possible for the supply of medical N95 masks to exceed Hubei’s requirement.
(28)2月5日,国家卫生健康委发布《新型冠状病毒感染肺炎诊疗方案(试行第五版)》。
(28)February 5: The NHC released Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Trial Version 5).
(29)2月7日,国务院联防联控机制印发《关于进一步强化责任落实做好防治工作的通知》,国家卫生健康委发布《新型冠状病毒感染肺炎防控方案(第四版)》。
(29)February 7: Through its Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism, the State Council issued Notice on Delivery of Duties for Effective Prevention and Control of the Disease. The NHC released Protocol on Prevention and Control of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Edition 4).
(30)2月8日,国家卫生健康委在亚太经合组织卫生工作组会议上介绍中国防疫努力和措施。国家卫生健康委向中国驻外使领馆通报新型冠状病毒防控、诊疗、监测、流行病学调查、实验室检测等方案。中美两国卫生部门负责人再次就美方专家参加中国-世界卫生组织联合专家考察组的安排进行沟通。
(30)February 8: The NHC gave briefings on China’s epidemic control efforts and measures at a meeting of the APEC health working group. It also gave briefings to Chinese diplomatic missions overseas on the guidelines for prevention and control, diagnosis and treatment, monitoring, epidemiological investigation and laboratory testing of the novel coronavirus.
Heads of Chinese and US health authorities further exchanged views on arrangements for American experts to join the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease.
(31)2月10日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席习近平在北京调研指导新冠肺炎疫情防控工作,并通过视频连线武汉市收治新冠肺炎患者的金银潭医院、协和医院、火神山医院,强调要以更坚定的信心、更顽强的意志、更果断的措施,紧紧依靠人民群众,坚决打赢疫情防控的人民战争、总体战、阻击战;指出湖北和武汉是疫情防控的重中之重,是打赢疫情防控阻击战的决胜之地,武汉胜则湖北胜,湖北胜则全国胜,要打好武汉保卫战、湖北保卫战;强调要按照集中患者、集中专家、集中资源、集中救治“四集中”原则,全力做好救治工作;强调要坚决抓好“外防输入、内防扩散”两大环节,尽最大可能切断传染源,尽最大可能控制疫情波及范围。
(31)February 10: Xi Jinping inspected prevention and control work in Beijing. He also talked by video link to doctors from Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital, Wuhan Union Hospital and Huoshenshan Hospital where novel coronavirus patients were being treated. He called for strengthening confidence and taking more decisive measures to stem the spread of and win the people’s all-out war against the virus. He emphasized that top priority must be given to Hubei and Wuhan, as they were the decisive battlegrounds. Victory in Wuhan would ensure victory in Hubei, and ultimately victory across the country. No effort would be spared in saving lives. The infected should be treated in designated hospitals by top-level doctors and with all necessary resources guaranteed. Strict measures must be taken to forestall inbound and intra-city transmissions, neutralize all sources of infection and stem the spread of the virus to the greatest extent possible.
(32)2月10日,建立省际对口支援湖北省除武汉市以外地市新冠肺炎医疗救治工作机制,统筹安排19个省份对口支援湖北省武汉市以外16个市州及县级市。
(32)February 10: A mechanism was established to organize pairing assistance from other provinces to Hubei’s cities other than Wuhan for treatment of the infected. Assistance from 19 provinces was rendered to 16 cities in Hubei.
(33)2月11日,国务院联防联控机制加强协调调度,供应湖北省医用防护服首次实现供大于求。
(33)February 11: Thanks to strengthened coordination under the State Council Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism, the supply of medical protective suits to Hubei exceeded its needs.
(34)2月11日,中国疾控中心专家应约与美国疾控中心流感部门专家召开电话会议,沟通和分享疫情防控信息。
(34)February 11: China CDC experts had a teleconference at the request of flu experts from the US CDC, during which they shared information on novel coronavirus prevention and control.
(35)2月12日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,指出疫情防控工作到了最吃劲的关键阶段,要毫不放松做好疫情防控重点工作,加强疫情特别严重或风险较大的地区防控;强调要围绕“提高收治率和治愈率”“降低感染率和病亡率”,抓好疫情防控重点环节;强调要全面增强收治能力,坚决做到“应收尽收、应治尽治”,提高收治率;强调要提高患者特别是重症患者救治水平,集中优势医疗资源和技术力量救治患者;强调人口流入大省大市要按照“联防联控、群防群控”要求,切实做好防控工作。
(35)February 12: At a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee, Xi Jinping noted that China’s novel coronavirus prevention and control had reached the most crucial stage. Key epidemic control tasks must be fulfilled, and greater attention must be given to the hardest-hit and high-risk areas. He called for improvements in key links in disease control to raise the admission and cure rates and lower the infection and fatality rates. Hospital capacity must be boosted to ensure admission and treatment for all patients. The best medical resources and technologies should be pooled to treat all infections, particularly the most severe cases. He urged those provinces and cities with large population inflows to strengthen cross-region joint prevention and control and society-wide efforts to contain the virus.
(36)2月13日,美国卫生与公众服务部相关负责人致函中国国家卫生健康委负责人,沟通双方卫生和疫情防控合作等有关安排。
(36)February 13: The head of the NHC received a letter from the head of the US HHS on arrangements concerning bilateral cooperation on public health and novel coronavirus prevention and control.
(37)2月14日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席、中央全面深化改革委员会主任习近平主持召开中央全面深化改革委员会第十二次会议,指出确保人民生命安全和身体健康,是中国共产党治国理政的一项重大任务;强调既要立足当前,科学精准打赢疫情防控阻击战,更要放眼长远,总结经验、吸取教训,针对这次疫情暴露出来的短板和不足,抓紧补短板、堵漏洞、强弱项,完善重大疫情防控体制机制,健全国家公共卫生应急管理体系。
(37)February 14: Xi Jinping chaired the 12th meeting of the Commission for Further Reform under the CPC Central Committee. He emphasized that protecting people’s lives and health is a high priority on the CPC’s governance agenda. Immediate, science-based and targeted measures must be taken to stamp out the virus. Experience and lessons must be drawn to enhance preparedness in the future. Swift actions must be taken to address problems, plug loopholes, and reinforce weak links. He also emphasized the need to improve both the mechanism for preventing and controlling major epidemics and the national public health emergency response system.
(38)2月14日,全国除湖北省以外其他省份新增确诊病例数实现“十连降”。
(38)February 14: All provinces and equivalent administrative units other than Hubei saw a continuous drop in newly confirmed cases for the 10th consecutive day.
(39)2月15日,国务院新闻办公室首次在湖北省武汉市举行疫情防控新闻发布会。至2月15日,已有7个诊断检测试剂获批上市,部分药物筛选与治疗方案、疫苗研发、动物模型构建等取得阶段性进展。
(39)February 15: The State Council Information Office held its first press conference on novel coronavirus prevention and control in Wuhan. By that day, seven types of test reagents had been approved for market launch, and progress had been made in drug screening, development of therapeutic regimens and vaccines, and animal model construction.
(40)2月16日开始,由中国、德国、日本、韩国、尼日利亚、俄罗斯、新加坡、美国和世界卫生组织25名专家组成的中国-世界卫生组织联合专家考察组,利用9天时间,对北京、成都、广州、深圳和武汉等地进行实地考察调研。
(40)February 16: The WHO-China Joint Mission on Covid-19, consisting of 25 experts from China, Germany, Japan, ROK, Nigeria, Russia, Singapore, the US and the WHO, started its nine-day field visit to Beijing, Chengdu, Guangzhou, Shenzhen and Wuhan.
(41)2月17日,国务院联防联控机制印发《关于科学防治精准施策分区分级做好新冠肺炎疫情防控工作的指导意见》,部署各地区各部门做好分区分级精准防控,有序恢复生产生活秩序。
(41)February 17: Through its Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism, the State Council issued Guidelines on Taking Science-based, Targeted, Region-specific, and Tiered Measures for Covid-19 Prevention and Control. Local authorities and government departments were required to take measures matching the corresponding levels of emergency response and ensure an orderly return to work and normal life.
(42)2月18日,全国新增治愈出院病例数超过新增确诊病例数,确诊病例数开始下降。中国国家卫生健康委复函美国卫生与公众服务部,就双方卫生与疫情合作有关安排进一步沟通。
(42)February 18: Nationwide, the daily number of newly cured and discharged coronavirus patients exceeded that of newly confirmed cases, and the number of confirmed cases began to drop. The NHC sent a reply to the US HHS on further arrangements concerning bilateral health and anti-virus cooperation.
(43)2月19日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,听取疫情防控工作汇报,研究统筹做好疫情防控和经济社会发展工作。
(43)February 19: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. The meeting heard reports on coronavirus prevention and control, and studied plans on strengthening virus control while promoting economic and social development.
(44)2月19日,国家卫生健康委发布《新型冠状病毒肺炎诊疗方案(试行第六版)》。
(44)February 19: The NHC released Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Covid-19 (Trial Version 6).
(45)2月19日,武汉市新增治愈出院病例数首次大于新增确诊病例数。
(45) February 19: For the first time in Wuhan, newly cured and discharged cases outnumbered newly confirmed ones.
(三)第三阶段:本土新增病例数逐步下降至个位数
(2月21日至3月17日)
Stage III: Newly Confirmed Domestic Cases on the Chinese Mainland Drop to Single Digits
(February 21-March 17, 2020)
湖北省和武汉市疫情快速上升势头均得到遏制,全国除湖北省以外疫情形势总体平稳,3月中旬每日新增病例控制在个位数以内,疫情防控取得阶段性重要成效。根据疫情防控形势发展,中共中央作出统筹疫情防控和经济社会发展、有序复工复产重大决策。(图6)
China had made significant progress: The rapid spread of the virus had been contained in Wuhan and the rest of Hubei Province, the situation in other parts on the mainland had stabilized, and the daily figure for new cases had remained in single digits since mid-March. As the situation evolved, the CPC Central Committee decided to coordinate epidemic control with economic and social development, and organize an orderly return to normal work and daily life (see Chart 6).
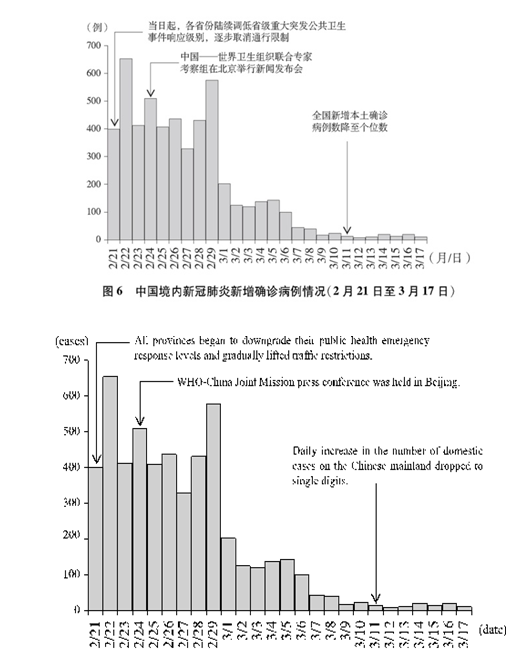
Chart 6. Daily Figure for Newly Confirmed Cases on the Chinese Mainland
(February 21-March 17)
(1)2月21日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局会议,指出疫情防控工作取得阶段性成效,同时,全国疫情发展拐点尚未到来,湖北省和武汉市防控形势依然严峻复杂;强调要针对不同区域情况,完善差异化防控策略,坚决打好湖北保卫战、武汉保卫战,加强力量薄弱地区防控,全力做好北京疫情防控工作;强调要建立与疫情防控相适应的经济社会运行秩序,有序推动复工复产。
(1)February 21: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He pointed out that while significant progress had been made in containing the epidemic, the turning point had not yet arrived at the national level. Wuhan and the entire province of Hubei still faced a grave and complex threat. He instructed that differentiated control measures be adopted to address the problems in different regions, to defend Hubei and its capital city, to step up support to regions with insufficient capacity, and to make an all-out effort to ensure the safety of Beijing, the national capital. He required that the economic and social order be managed in parallel with the anti-epidemic endeavor, and called for an orderly return to normal work and daily life.
(2)2月21日,国务院联防联控机制印发《企事业单位复工复产疫情防控措施指南》,国家卫生健康委发布《新型冠状病毒肺炎防控方案(第五版)》。
(2)February 21: Through its Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism, the State Council issued Guidelines on Covid-19 Prevention and Control Measures for Resumption of Work.
The NHC released Protocol on Prevention and Control of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Edition 5).
(3)2月21日起,各地因地制宜,陆续调低省级重大突发公共卫生事件响应级别,逐步取消通行限制。至2月24日,除湖北省、北京市外,其他省份主干公路卡点全部打通,运输秩序逐步恢复。
(3)February 21: Most provinces and equivalent administrative units started to downgrade their public health emergency response level in light of the local situation, and gradually lifted traffic restrictions. By February 24, all provincial trunk highways had reopened, and order was restored to the transport networks with the exception of those in Hubei and Beijing.
(4)2月23日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席习近平出席统筹推进新冠肺炎疫情防控和经济社会发展工作部署会议,通过视频直接面向全国17万名干部进行动员部署,指出新冠肺炎疫情是新中国成立以来在我国发生的传播速度最快、感染范围最广、防控难度最大的一次重大突发公共卫生事件,这是一次危机,也是一次大考,经过艰苦努力,疫情防控形势积极向好的态势正在拓展;强调疫情形势依然严峻复杂,防控正处在最吃劲的关键阶段,要坚定必胜信念,咬紧牙关,继续毫不放松抓紧抓实抓细各项防控工作;强调要变压力为动力、善于化危为机,有序恢复生产生活秩序,强化“六稳”举措,加大政策调节力度,把发展巨大潜力和强大动能充分释放出来,努力实现今年经济社会发展目标任务。
(4) February 23: President Xi spoke to 170,000 officials nationwide by video link, at a meeting on coordinating epidemic control with economic and social development. He emphasized that this epidemic, given the speed and scope of its spread, represented the most challenging public health emergency in China since the founding of the People’s Republic, and that it was both a serious crisis and a major test. He acknowledged the arduous efforts of all involved, welcoming the fact that control measures were producing increasingly positive results, but noting that the overall situation remained complex and serious, and this stage would be crucial in curbing the spread. The people must maintain their faith in ultimate victory and make unremitting efforts in all of their prevention and control work. He encouraged the nation to turn pressure into strength and adversity into opportunities, and steadily resume normal work and daily life. He demanded a redoubled effort to stabilize the six fronts -- employment, finance, foreign trade, inbound investment, domestic investment, and market expectations, called for stronger policies to unleash the full potential and maintain the strong momentum of China’s development, and urged the nation to achieve the goals and tasks set for this year’s economic and social development.
(5)2月24日,中国-世界卫生组织联合专家考察组在北京举行新闻发布会,认为中国在减缓疫情扩散蔓延、阻断病毒人际传播方面取得明显效果,已经避免或至少推迟了数十万人感染新冠肺炎。至2月24日,全国新增确诊病例数已连续5天在1000例以下,现有确诊病例数近一周以来呈现下降趋势,所有省份新增出院病例数均大于或等于新增确诊病例数。
(5)February 24: The WHO-China Joint Mission on Covid-19 held a press conference in Beijing, during which team members agreed that China had achieved notable success in slowing the spread of the virus and blocking human-to-human transmission, at least delaying and possibly preventing hundreds of thousands of infections. “This approach, what we call an ‘all-of-government, all-of-society’ approach, very old-fashioned, too old in some ways, has probably, definitely reverted, and probably prevented at least tens of thousands, but probably hundreds of thousands of cases of Covid-19 in China”. By February 24, the daily number of new infections on the Chinese mainland had remained below 1,000 for five consecutive days, the number of existing confirmed cases had kept dropping for almost a week, and the daily figure for discharged patients was now equal to or had surpassed that of new infections in all provincial-level administrative units.
(6)2月25日起,全面加强出入境卫生检疫工作,对出入境人员严格健康核验、体温监测、医学巡查、流行病学调查、医学排查、采样监测,防止疫情跨境传播。
(6)February 25: China started to tighten up border quarantine, conducting a strict check of health and body temperature, and carrying out medical inspection, epidemiological investigation, medical screening, and sample monitoring of all inbound and outbound travelers, in order to minimize the cross-border spread of the epidemic.
(7)2月26日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,指出全国疫情防控形势积极向好的态势正在拓展,经济社会发展加快恢复,同时湖北省和武汉市疫情形势依然复杂严峻,其他有关地区疫情反弹风险不可忽视;强调要继续集中力量和资源,全面加强湖北省和武汉市疫情防控;强调要准确分析把握疫情和经济社会发展形势,紧紧抓住主要矛盾和矛盾的主要方面,确保打赢疫情防控的人民战争、总体战、阻击战,努力实现决胜全面建成小康社会、决战脱贫攻坚目标任务。
(7)February 26: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He told the meeting that the national situation in epidemic control was turning for the better and economic and social development was quickly returning to normal, while Wuhan and Hubei as a whole still faced a grave and complex situation, and the possibility of an epidemic resurgence must not be overlooked in other regions. He called for a greater effort to marshal the resources of the whole country to reinforce Wuhan and Hubei. He emphasized the need to make an accurate assessment of the epidemic dynamics and the conditions facing economic and social development, and focus on the main problems and the key elements of these problems, so as to ensure an overall victory in the battle against the virus, and achieve the goals of building a moderately prosperous society in all respects and of the country’s poverty alleviation.
(8)2月27日,全国除湖北省以外其他省份,湖北省除武汉市以外其他地市,新增确诊病例数首次双双降至个位数。
(8)February 27: The daily figure for new cases in Hubei other than Wuhan, and in other places on the mainland outside Hubei, both dropped to single digits for the first time.
(9)2月28日,国务院联防联控机制印发《关于进一步落实分区分级差异化防控策略的通知》。
(9)February 28: Through its Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism, the State Council released Notice on Furthering Differentiated, Region-specific and Tiered Prevention and Control Measures.
(10)2月29日,中国-世界卫生组织新型冠状病毒肺炎联合考察报告发布。报告认为,面对前所未知的病毒,中国采取了历史上最勇敢、最灵活、最积极的防控措施,尽可能迅速地遏制病毒传播;令人瞩目的是,在所考察的每一个机构都能够强有力地落实防控措施;面对共同威胁时,中国人民凝聚共识、团结行动,才使防控措施得以全面有效的实施;每个省、每个城市在社区层面都团结一致,帮助和支持脆弱人群及社区。
(10)February 29: The WHO-China Joint Mission on Covid-19 released a report about its field study trip in China. The report described China’s control efforts. It said, “In the face of a previously unknown virus, China has rolled out perhaps the most ambitious, agile and aggressive disease containment effort in history... As striking, has been the uncompromising rigor of strategy application that proved to be a hallmark in every setting and context where it was examined... Achieving China’s exceptional coverage with and adherence to these containment measures has only been possible due to the deep commitment of the Chinese people to collective action in the face of this common threat. At a community level this is reflected in the remarkable solidarity of provinces and cities in support of the most vulnerable populations and communities.”
(11)3月2日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席习近平在北京考察新冠肺炎防控科研攻关工作,强调要把新冠肺炎防控科研攻关作为一项重大而紧迫任务,在坚持科学性、确保安全性的基础上加快研发进度,为打赢疫情防控的人民战争、总体战、阻击战提供强大科技支撑;指出尽最大努力挽救更多患者生命是当务之急、重中之重,要加强药物、医疗装备研发和临床救治相结合,切实提高治愈率、降低病亡率;强调要加快推进已有的多种技术路线疫苗研发,争取早日推动疫苗的临床试验和上市使用;指出要把生物安全作为国家总体安全的重要组成部分,加强疫病防控和公共卫生科研攻关体系和能力建设。
(11)March 2: President Xi inspected several scientific institutions in Beijing, observing their research and development on Covid-19 prevention and control. He said that this work must be taken as a major and pressing task and proceed as speedily as possible, while abiding by the rules of science and ensuring safety, so as to provide strong scientific and technological support for overcoming the epidemic. Xi Jinping pointed out that saving as many lives as possible, by every possible means, was the number one priority. Research on and development of medicines and medical equipment should be integrated with clinical treatment, with the twin goals of raising the cure rate and lowering the fatality rate. Development of vaccines should be expedited through multiple approaches, so as to make them available for clinical trial and application as quickly as possible. The president said that biosecurity should be an important part of the holistic approach to national security, and he called for efforts to enhance China’s scientific research capacity regarding epidemic prevention and control and public health.
(12)3月3日,国家卫生健康委发布《新型冠状病毒肺炎诊疗方案(试行第七版)》,在传播途径、临床表现、诊断标准等多个方面作出修改和完善,强调加强中西医结合。
(12)March 3: The NHC released Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Covid-19 (Trial Version 7), which made modifications in the determination of transmission routes and clinical symptoms, updated diagnostic criteria, and emphasized the integration of traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine in treating the disease.
(13)3月4日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,指出要加快建立同疫情防控相适应的经济社会运行秩序,完善相关举措,巩固和拓展来之不易的良好势头;强调要持续用力加强湖北省和武汉市疫情防控工作,继续保持“内防扩散、外防输出”的防控策略。
(13)March 4: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He emphasized the need to quickly bring order to economic and social development in the context of epidemic control, improve relevant measures, and consolidate and extend the country’s hard-won progress. Wuhan and Hubei must continue their epidemic control, and continue the measures for preventing the virus from spreading within their local area or beyond.
(14)3月6日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席习近平出席决战决胜脱贫攻坚座谈会,指出到2020年现行标准下的农村贫困人口全部脱贫,是中共中央向全国人民作出的郑重承诺,必须如期实现;强调要以更大决心、更强力度推进脱贫攻坚,坚决克服新冠肺炎疫情影响,坚决夺取脱贫攻坚战全面胜利,坚决完成这项对中华民族、对人类都具有重大意义的伟业。
(14)March 6: Xi Jinping attended a symposium on securing a decisive victory in poverty alleviation. He pointed out that the solemn pledge to lift all rural people living below current poverty line out of poverty by 2020 had been made by the CPC Central Committee to the whole nation, and it must be fulfilled on schedule. He called for greater determination and intensity in advancing poverty alleviation, and highlighted the need to offset the impact of the epidemic in order to clinch a complete victory over poverty – a cause of such tremendous importance to China and all of humanity.
(15)3月6日,全国新增本土确诊病例数降至100例以下,11日降至个位数。
(15)March 6: The daily increase in the number of domestic cases on the Chinese mainland dropped below 100, and fell further to single digits on March 11.
(16)3月7日,国家卫生健康委发布《新型冠状病毒肺炎防控方案(第六版)》。
(16)March 7: The NHC released Protocol on Prevention and Control of Covid-19 (Edition 6).
(17)3月10日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席习近平赴湖北省武汉市考察疫情防控工作,指出经过艰苦努力,湖北和武汉疫情防控形势发生积极向好变化,取得阶段性重要成果,但疫情防控任务依然艰巨繁重,要慎终如始、再接再厉、善作善成,坚决打赢湖北保卫战、武汉保卫战;指出武汉人民识大体、顾大局,不畏艰险、顽强不屈,自觉服从疫情防控大局需要,主动投身疫情防控斗争,作出了重大贡献;指出抗击疫情有两个阵地,一个是医院救死扶伤阵地,一个是社区防控阵地,要充分发挥社区在疫情防控中的重要作用,使所有社区成为疫情防控的坚强堡垒;强调打赢疫情防控人民战争要紧紧依靠人民,把群众发动起来,构筑起群防群控的人民防线。
(17)March 10: Xi Jinping went to Wuhan to inspect work on epidemic control. He acknowledged that the situation in Hubei and Wuhan was improving and that hard work had delivered important results, and pointed out that the task remained arduous. He encouraged the people to persevere in their efforts and win the battles against the virus in Hubei and Wuhan. He praised residents in Wuhan for considering the national interest and the general situation. They had proved themselves indomitable and resilient, and they had consciously subordinated their needs to the overall interests of epidemic control, joined the battle against the epidemic, and made a huge contribution.
He pointed out that there were two fronts in the battle against the epidemic: the hospital and the community – the life-saving front and the epidemic prevention and control front. Communities should play their key role in epidemic prevention and control, and every community should serve as a bastion of defense against the virus. He called for a general mobilization, putting in place a defense line across the whole of society and relying on the people to win the battle.
(18)3月11日,世界卫生组织总干事谭德塞表示,新冠肺炎疫情已具有大流行特征。
(18)March 11: WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus announced, “We have therefore made the assessment that Covid-19 can be characterized as a pandemic.”
(19)3月11日至17日,全国每日新增本土确诊病例数维持在个位数。总体上,中国本轮疫情流行高峰已经过去,新增发病数持续下降,疫情总体保持在较低水平。
(19)March 11 to 17: The daily increase in the number of domestic cases on the Chinese mainland remained in single digits. The epidemic peak had passed in China as a whole, with the number of new cases steadily declining and the epidemic comfortably under control.
(20)3月17日,首批42支国家援鄂医疗队撤离武汉。
(20) March 17: Forty-two medical teams from around the country left Wuhan, having completed their mission there.
(四)第四阶段:取得武汉保卫战、湖北保卫战决定性成果
(3月18日至4月28日)
Stage IV: Wuhan and Hubei – An Initial Victory in a Critical Battle
(March 18-April 28, 2020)
以武汉市为主战场的全国本土疫情传播基本阻断,离汉离鄂通道管控措施解除,武汉市在院新冠肺炎患者清零,武汉保卫战、湖北保卫战取得决定性成果,全国疫情防控阻击战取得重大战略成果。境内疫情零星散发,境外疫情快速扩散蔓延,境外输入病例造成关联病例传播。中共中央把握疫情形势发展变化,确定了“外防输入、内防反弹”的防控策略,巩固深化国内疫情防控成效,及时处置聚集性疫情,分类推动复工复产,关心关爱境外中国公民。(图7)
By making critical advances in the city of Wuhan, the main battleground against the virus, China initially halted the spread of Covid-19 on the mainland. Restrictions on outbound traffic from Wuhan City and Hubei Province were lifted, and all Covid-19 patients in Wuhan hospitals were discharged. China won a critical battle in defending Wuhan and Hubei against Covid-19, which was a major step forward in the nationwide virus control effort. During this period, sporadic cases were reported, and more infections were caused by inbound arrivals carrying the virus which continued to spread overseas. In response to the evolving Covid-19 dynamics, the CPC Central Committee adopted an approach to prevent the coronavirus from entering the country and stem its domestic resurgence. Efforts were made to consolidate gains in virus control, promptly treat cluster cases, and get the country back to work sector by sector. Care and support were given to Chinese citizens abroad (see Chart 7).
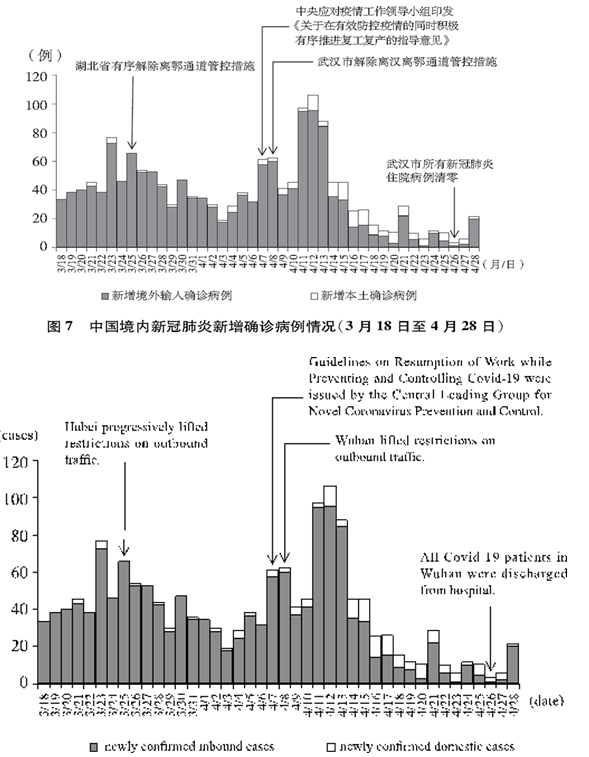
Chart 7. Daily Figure for Newly Confirmed Cases on the Chinese Mainland
(March 18-April 28)
(1)3月18日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,强调要落实外防输入重点任务,完善应对输入性风险的防控策略和政策举措,决不能让来之不易的疫情防控持续向好形势发生逆转;指出要加强对境外中国公民疫情防控的指导和支持,保护他们的生命安全和身体健康。
(1)March 18: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He emphasized the need to take rigorous steps to stop inbound cases, so that hard-won gains in virus control would not be lost. He urged stronger measures to protect the health of Chinese citizens overseas.
(2)3月18日,国务院办公厅印发《关于应对新冠肺炎疫情影响强化稳就业举措的实施意见》。
(2)March 18: The State Council issued Decision on Implementation of Measures to Stabilize Employment by Offsetting the Impact of Covid-19.
(3)3月18日,全国新增本土确诊病例首次实现零报告。至19日,湖北省以外省份连续7日无新增本土确诊病例。
(3)March 18: For the first time, no new domestic cases were confirmed on the Chinese mainland. By March 19, no new cases had been confirmed for seven days outside of Hubei Province.
(4)3月25日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,听取疫情防控工作和当前经济形势的汇报,研究当前疫情防控和经济工作。
(4)March 25: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee to hear briefings about virus control and current economic conditions and discuss virus control measures and ways to sustain economic growth.
(5)3月25日起,湖北省有序解除离鄂通道管控措施,撤除除武汉市以外地区所有通道(市际、省界通道)检疫站点。湖北省除武汉市以外地区逐步恢复正常生产生活秩序,离鄂人员凭湖北健康码“绿码”安全有序流动。
(5)March 25: Hubei lifted outbound traffic restrictions and removed all health checkpoints on highways across the province except in Wuhan. With the exception of Wuhan, work and life gradually returned to normal in the whole province, and people could now leave Hubei if they had a “green” health code to show that they were not infected.
(6)3月25日,23个省份报告了境外输入确诊病例,防止疫情扩散压力依然很大。
(6)March 25: Confirmed inbound cases were reported in 23 provinces, signaling the need to curb the spread of the virus.
(7)3月26日,国家主席习近平出席二十国集团领导人特别峰会,发表题为《携手抗疫 共克时艰》的讲话。
(7)March 26: President Xi attended the G20 Extraordinary Leaders’ Summit on Covid-19 and delivered a speech titled “Working Together to Defeat the Covid-19 Outbreak”.
(8)3月27日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局会议,指出要因应国内外疫情防控新形势,及时完善疫情防控策略和应对举措,把重点放在“外防输入、内防反弹”上来,保持疫情防控形势持续向好态势;强调要在疫情防控常态化条件下加快恢复生产生活秩序,力争把疫情造成的损失降到最低限度,努力完成全年经济社会发展目标任务;强调要在做好疫情防控的前提下,支持湖北有序复工复产,做好援企、稳岗、促就业、保民生等工作。
(8)March 27: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He called for a timely improvement in China’s Covid-19 control measures in response to changing Covid-19 dynamics, both domestic and globally, with a shift in focus to preventing inbound cases and domestic resurgence, so as to sustain the positive momentum in virus control. He stressed the need to speedily resume work and normal life while continuing Covid-19 prevention and control, in order to minimize the losses caused by Covid-19 and fulfill the goals of economic and social development set for the year. Provided that prevention and control protocols were duly observed, support should be given to get Hubei back to work in an orderly manner, and help enterprises create jobs, keep their employees, and ensure their livelihoods.
(9)3月29日至4月1日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席习近平前往浙江,就统筹推进新冠肺炎疫情防控和经济社会发展工作进行调研,指出要把严防境外疫情输入作为当前乃至较长一段时间疫情防控的重中之重,增强防控措施的针对性和实效性,筑起应对境外疫情输入风险的坚固防线;强调要准确识变、科学应变、主动求变,善于从眼前的危机、眼前的困难中捕捉和创造机遇;强调要在严格做好疫情防控工作的前提下,有力有序推动复工复产提速扩面,积极破解复工复产中的难点、堵点,推动全产业链联动复工。
(9)March 29 to April 1: Xi Jinping made an inspection tour to Zhejiang Province to review its Covid-19 control and economic and social development.
He stressed that guarding against inbound infections should be the top priority for the country both now and in the foreseeable future and that control must be targeted and effective so as to build a strong line of defense against inbound cases. He emphasized the need to remain sensitive to changes, respond to them with well-judged actions, be ready to adjust the approach when necessary, and identify and seize opportunities in the current crisis. He urged a steady return to work in more sectors while strictly continuing virus control measures and resolving problems hindering the return to work, so as to restore the operation of complete industrial chains.
(10)4月1日,中国海关在所有航空、水运、陆路口岸对全部入境人员实施核酸检测。
(10)April 1: Chinese customs began nucleic acid testing (NAT) on inbound arrivals at all points of entry – air, water and land.
(11)4月4日清明节,举行全国性哀悼活动,全国各地各族人民深切悼念抗击新冠肺炎疫情斗争牺牲烈士和逝世同胞。
(11)April 4: A nationwide ceremony was held on the traditional Tomb-sweeping Day to pay tribute to all those who had given their lives in fighting Covid-19, and others who had died of the novel coronavirus.
(12)4月6日,国务院联防联控机制印发《关于进一步做好重点场所重点单位重点人群新冠肺炎疫情防控相关工作的通知》和《新冠病毒无症状感染者管理规范》。
(12)April 6: Through its Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism, the State Council issued Notice on Prevention and Control Measures for Key Locations, Organizations and Population Groups, and Manual for Management of Asymptomatic Virus Carriers.
(13)4月7日,中央应对疫情工作领导小组印发《关于在有效防控疫情的同时积极有序推进复工复产的指导意见》,国务院联防联控机制印发《全国不同风险地区企事业单位复工复产疫情防控措施指南》。各地做好复工复产相关疫情防控,分区分级恢复生产秩序。
(13)April 7: The Central Leading Group for Novel Coronavirus Prevention and Control issued Guidelines on Resumption of Work while Preventing and Controlling Covid-19; and the State Council released Guidelines on Covid-19 Prevention and Control Measures for Localities at Different Risk Levels to Resume Work. Region-specific and tiered measures for Covid-19 control were adopted to pave the way for a return to normal work in different locations.
(14)4月8日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,指出要坚持底线思维,做好较长时间应对外部环境变化的思想准备和工作准备;强调“外防输入、内防反弹”防控工作决不能放松;强调要抓好无症状感染者精准防控,把疫情防控网扎得更密更牢,堵住所有可能导致疫情反弹的漏洞;强调要加强陆海口岸疫情防控,最大限度减少境外输入关联本地病例。(14)April 8: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He reiterated the need to stay alert against potential risks and be prepared, both in thinking and action, to respond to long-term changes in the external environment. He warned against any relaxation of the efforts to both stop inbound cases and forestall domestic resurgence of cases. Targeted measures should be taken to manage asymptomatic cases, build a strong line of defense and plug any loopholes that might cause a resurgence of the virus. Control at land and sea points of entry should be tightened to minimize domestic cases caused by inbound arrivals carrying the virus.
(15)4月8日起,武汉市解除持续76天的离汉离鄂通道管控措施,有序恢复对外交通,逐步恢复正常生产生活秩序。
(15)April 8: Wuhan lifted its 76-day outbound traffic restrictions; and local work and daily life began to return to normal.
(16)4月10日,湖北省在院治疗的重症、危重症患者首次降至两位数。
(16)April 10: The number of patients in severe or critical condition in Hubei dropped to double digits for the first time.
(17)4月14日,国务院总理李克强在北京出席东盟与中日韩(10+3)抗击新冠肺炎疫情领导人特别会议并发表讲话,介绍中国统筹推进疫情防控和经济社会发展的经验,提出全力加强防控合作、努力恢复经济发展、着力密切政策协调等合作倡议。
(17)April 14: Premier Li Keqiang delivered a speech at a special meeting attended by leaders of ASEAN nations, China, Japan, the Republic of Korea on fight against the novel coronavirus. He shared with these leaders China’s experience in coordinating the fight against the virus with its efforts to continue economic and social development. He proposed to strengthen cooperation on the fight against the virus, on efforts to resume economic development, and on policy coordination among the participating countries.
(18)4月15日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,听取疫情防控工作和当前经济形势汇报,研究疫情防控和经济工作。
(18)April 15: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee to hear briefings on virus control and current economic conditions, and discuss virus response measures and ways to sustain economic growth.
(19)4月17日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局会议,强调要抓紧抓实抓细常态化疫情防控,因时因势完善“外防输入、内防反弹”各项措施并切实抓好落实,不断巩固疫情持续向好形势;强调要坚持稳中求进工作总基调,在稳的基础上积极进取,在常态化疫情防控中全面推进复工复产达产,恢复正常经济社会秩序,培育壮大新的增长点增长极,牢牢把握发展主动权。
(19)April 17: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He called for full implementation of virus control measures to prevent both inbound cases and domestic resurgence and to build positive momentum in Covid-19 control. He emphasized the need to follow the general principles of pursuing stable performance and making new progress, returning to work while continuing Covid-19 control, restoring economic and social order, fostering new growth areas, and actively promoting development.
(20)4月17日,武汉市新冠肺炎疫情防控指挥部发布《关于武汉市新冠肺炎确诊病例数确诊病例死亡数订正情况的通报》,对确诊和死亡病例数进行订正。截至4月16日24时,确诊病例核增325例,累计确诊病例数订正为50333例;确诊病例的死亡病例核增1290例,累计确诊病例的死亡数订正为3869例。
(20)April 17: Wuhan City Novel Coronavirus Prevention and Control Command Center released Briefing on Modifying the Figures of Confirmed Covid-19 Cases and Fatalities in Wuhan. By midnight on April 16, the total number of confirmed cases in the city had been revised up by 325 to 50,333, and the number of deaths up by 1,290 to 3,869.
(21)4月20日至23日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席习近平在陕西考察,指出要坚持稳中求进工作总基调,坚持新发展理念,扎实做好稳就业、稳金融、稳外贸、稳外资、稳投资、稳预期工作,全面落实保居民就业、保基本民生、保市场主体、保粮食能源安全、保产业链供应链稳定、保基层运转任务,努力克服新冠肺炎疫情带来的不利影响,确保完成决战决胜脱贫攻坚目标任务,全面建成小康社会。
(21)April 20-23: Xi Jinping made an inspection tour to Shaanxi Province. He urged local officials to pursue steady performance, make new progress, and act according to the new development philosophy. He called on them to carry out the following tasks: stabilizing employment, finance, foreign trade, inbound investment, domestic investment, and market expectations, and guaranteeing jobs, daily living needs, food and energy, industrial and supply chains, the interests of market players, and the smooth functioning of grassroots government. By so doing, China could offset the adverse impact of Covid-19 and fulfill the goals of eliminating poverty and achieving moderate prosperity.
(22)4月23日,国务院总理李克强主持召开部分省市经济形势视频座谈会,推动做好当前经济社会发展工作。
(22)April 23: Premier Li Keqiang chaired a video conference on the economic situation in some provinces and cities in order to promote economic and social development in these regions.
(23)4月26日,武汉市所有新冠肺炎住院病例清零。
(23)April 26: The last hospitalized Covid-19 patient in Wuhan was discharged.
(24)4月27日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席、中央全面深化改革委员会主任习近平主持召开中央全面深化改革委员会第十三次会议,强调中国疫情防控和复工复产之所以能够有力推进,根本原因是中国共产党的领导和中国社会主义制度的优势发挥了无可比拟的重要作用;强调发展环境越是严峻复杂,越要坚定不移深化改革,健全各方面制度,完善治理体系,促进制度建设和治理效能更好转化融合,善于运用制度优势应对风险挑战冲击。
(24)April 27: Xi Jinping chaired the 13th meeting of the Commission for Further Reform under the CPC Central Committee. He pointed out that the CPC leadership and China’s socialist system had played a critical role in Covid-19 control and the resumption of business activities in China. As the environment for development became more complicated, China should be more resolute in furthering reform and improving its governing systems, and it should fully leverage its strengths to deal with risks and challenges.
(25)4月27日,经中共中央总书记习近平和中共中央批准,中央指导组离鄂返京。
(25) April 27: The Central Steering Group returned to Beijing from Hubei.
(五)第五阶段:全国疫情防控进入常态化
(4月29日以来)
Stage V: Ongoing Prevention and Control
(Since April 29, 2020)
境内疫情总体呈零星散发状态,局部地区出现散发病例引起的聚集性疫情,境外输入病例基本得到控制,疫情积极向好态势持续巩固,全国疫情防控进入常态化。加大力度推进复工复产复学,常态化防控措施经受“五一”假期考验。经中共中央批准,国务院联防联控机制派出联络组,继续加强湖北省疫情防控。(图8)
Sporadic cases have been reported on the mainland, resulting in case clusters in some locations. Inbound cases are generally under control. The positive momentum in Covid-19 control has thus been locked in, and nationwide virus control is now being conducted on an ongoing basis. China has made vigorous efforts to resume work and reopen schools. The ongoing control measures passed the test of the travel peak during the May Day holiday. With the approval of the CPC Central Committee, an inter-departmental contact group under the Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism of the State Council was dispatched to Hubei to oversee local virus control (see Chart 8).

Chart 8. Daily Figure for Newly Confirmed Cases on the Chinese Mainland
(April 29-May 31)
(1)4月29日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,指出经过艰苦卓绝的努力,湖北保卫战、武汉保卫战取得决定性成果,全国疫情防控阻击战取得重大战略成果;强调要抓好重点地区、重点群体疫情防控工作,有针对性加强输入性风险防控工作。
(1)April 29: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He concluded that thanks to arduous efforts, China had won a vital battle in defending Wuhan and Hubei against the novel coronavirus, and achieved a major strategic success in the nationwide control efforts. At the same time, he emphasized that virus control should continue in key regions and target key groups, with a focus on inbound cases.
(2)4月30日,京津冀地区突发公共卫生事件应急响应级别由一级响应调整为二级响应。
(2) April 30: The public health emergency response was lowered to Level 2 in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region.
(3)5月1日,世界卫生组织宣布,鉴于当前国际疫情形势,新冠肺炎疫情仍然构成“国际关注的突发公共卫生事件”。
(3)May 1: The WHO announced that given the current international Covid-19 dynamics, the novel coronavirus still remained a “public health emergency of international concern”.
(4)5月2日,湖北省突发公共卫生事件应急响应级别由一级响应调整为二级响应。
(4)May 2: The public health emergency response was lowered to Level 2 in Hubei.
(5)5月4日,经中共中央批准,国务院联防联控机制设立联络组,赴湖北省武汉市开展工作。
(5)May 4: An inter-departmental contact group under the Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism of the State Council was dispatched to Wuhan with the approval of the CPC Central Committee.
(6)5月6日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,指出在党中央坚强领导和全国各族人民大力支持下,中央指导组同湖北人民和武汉人民并肩作战,下最大气力控制疫情流行,努力守住全国疫情防控第一道防线,为打赢疫情防控的人民战争、总体战、阻击战作出了重要贡献;指出中共中央决定继续派出联络组,加强对湖北省和武汉市疫情防控后续工作指导支持,继续指导做好治愈患者康复和心理疏导工作,巩固疫情防控成果,决不能前功尽弃。
(6)May 6: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He pointed out that under the strong leadership of the Central Committee and with the support of all the people, the Central Steering Group had been working with the people of Wuhan and other parts of Hubei Province. They had done their utmost in the fight to curb the spread of the virus and erected a first line of defense for the nation, making a significant contribution to beating the virus. He said the contact group should guide and support follow-up work in Wuhan and other parts of Hubei and advise on the rehabilitation and psychological counseling of patients in recovery, to ensure that the gains would be consolidated.
(7)5月7日,国务院联防联控机制印发《关于做好新冠肺炎疫情常态化防控工作的指导意见》。
(7)May 7: Through the Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism, the State Council released Guidelines on Conducting Covid-19 Prevention and Control on an Ongoing Basis.
(8)5月8日,中共中央召开党外人士座谈会,就新冠肺炎疫情防控工作听取各民主党派中央、全国工商联和无党派人士代表的意见和建议,中共中央总书记习近平主持座谈会并发表重要讲话,强调面对突如其来的疫情,中共中央高度重视,坚持把人民生命安全和身体健康放在第一位,果断采取一系列防控和救治举措,用一个多月的时间初步遏制了疫情蔓延势头,用两个月左右的时间将本土每日新增病例控制在个位数以内,用3个月左右的时间取得了武汉保卫战、湖北保卫战的决定性成果;指出对一个拥有14亿人口的大国来说,这样的成绩来之不易。
(8)May 8: The CPC Central Committee held a meeting to hear the views and proposals from the central committees of China’s eight other political parties, representatives of the All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce, and prominent figures without party affiliation. General Secretary Xi chaired and addressed the meeting. He said that when the novel coronavirus struck, catching the country unawares, the CPC Central Committee gave its full attention to the matter. Putting people’s lives and health first, it swiftly adopted a series of policies on prevention and control of the virus and treatment of the infected. It took the country over a month to achieve initial success in curbing the spread of the virus, about two months to bring the daily figure of new domestic cases on the mainland down to single digits, and three months to win a decisive victory in defending Wuhan City and Hubei Province. For China, with a large population of 1.4 billion, this achievement did not come easily.
(9)5月11日至12日,中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席习近平赴山西,就统筹推进常态化疫情防控和经济社会发展工作、巩固脱贫攻坚成果进行调研,强调要坚持稳中求进工作总基调,坚持新发展理念,坚持以供给侧结构性改革为主线,扎实做好“六稳”工作,全面落实“六保”任务,努力克服新冠肺炎疫情带来的不利影响,在高质量转型发展上迈出更大步伐,确保完成决战决胜脱贫攻坚目标任务,全面建成小康社会。
(9)May 11-12: Xi Jinping made an inspection tour to Shanxi Province to be briefed on what had been done in the province to conduct Covid-19 prevention and control on an ongoing basis while promoting economic and social development, and to consolidate gains in poverty alleviation.
He urged local officials to act according to the new development philosophy for making steady progress, and carry out supply-side structural reform. They were required to stabilize the six fronts (employment, finance, foreign trade, inbound investment, domestic investment, and market expectations), and guarantee the six priorities (jobs, daily living needs, food and energy, industrial and supply chains, the interests of market players, and the smooth functioning of grassroots government). He called on local officials to overcome the adverse impact of the virus, accelerate high-quality economic transformation, and meet the goals of eliminating poverty and achieving moderate prosperity in all respects.
(10)5月14日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局常务委员会会议,指出要加强重点地区、重点场所内防反弹工作,近期发生聚集性疫情的地区要有针对性加强防控措施;强调要针对境外疫情的新情况新趋势,采取更加灵活管用的措施,强化外防输入重点领域和薄弱环节。
(10)May 14: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee. He urged that Covid-19 control be strengthened in key areas and key places to prevent its resurgence, and that targeted measures be taken where case clusters had recently occurred. Flexible and effective measures should be adopted to respond to evolving Covid-19 dynamics overseas, and key sectors and weak links in the prevention of inbound infection should be shored up.
(11)5月15日,中共中央总书记习近平主持召开中共中央政治局会议,讨论国务院拟提请第十三届全国人民代表大会第三次会议审议的《政府工作报告》稿,指出做好今年工作,要紧扣全面建成小康社会目标任务,统筹推进疫情防控和经济社会发展工作,在常态化疫情防控前提下,坚持稳中求进工作总基调,坚持新发展理念,坚持以供给侧结构性改革为主线,坚持以改革开放为动力推动高质量发展,坚决打好三大攻坚战,扎实做好“六稳”工作,全面落实“六保”任务,坚定实施扩大内需战略,维护经济发展和社会稳定大局,确保完成决战决胜脱贫攻坚目标任务,全面建成小康社会。
(11)May 15: Xi Jinping chaired a meeting of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee to discuss the draft Report on the Work of the Government, which the State Council would submit to the forthcoming Third Session of the 13th National People’s Congress for deliberation.
He pointed out that to fulfill the tasks of the year, the nation must carry out Covid-19 prevention and control as well as promoting economic and social development to reach the goal of achieving moderate prosperity in all respects. He said that while conducting control on an ongoing basis, the country should continue to deliver steady performance, act according to the new development philosophy, conduct supply-side structural reform, promote high-quality development through further reform and opening up, and continue the three critical battles against poverty, pollution and major risks. There should be solid progress in stabilizing the six fronts and guaranteeing the six priorities. Domestic consumption must be expanded, and economic development and social stability must be maintained, so as to fulfill the goals of eliminating poverty and achieving moderate prosperity in all respects.
(12)5月18日,国家主席习近平在第73届世界卫生大会视频会议开幕式上发表题为《团结合作战胜疫情 共同构建人类卫生健康共同体》的致辞。
(12)May 18: President Xi delivered a speech titled “Fighting Covid-19 through Solidarity and Cooperation, Building a Global Community of Health for All” at the opening of the 73rd World Health Assembly.
(13)5月21日至27日,全国政协十三届三次会议在北京举行。5月22日至28日,十三届全国人大三次会议在北京举行。
(13) May 21-27: The Third Session of the 13th National Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference was held in Beijing. May 22-28: The Third Session of the 13th National People’s Congress was held in Beijing.
二、防控和救治两个战场协同作战
II. Well-Coordinated Prevention, Control and Treatment
面对突发疫情侵袭,中国把人民生命安全和身体健康放在第一位,统筹疫情防控和医疗救治,采取最全面最严格最彻底的防控措施,前所未有地采取大规模隔离措施,前所未有地调集全国资源开展大规模医疗救治,不遗漏一个感染者,不放弃每一位病患,实现“应收尽收、应治尽治、应检尽检、应隔尽隔”,遏制了疫情大面积蔓延,改变了病毒传播的危险进程。“通过全面执行(中国)这些措施可以争取到一些时间,即使只有几天或数周,但这对最终减少新冠肺炎感染人数和死亡人数的价值不可估量。”(注1)
The coronavirus caught China unawares. Putting people’s lives and health first, the Chinese government has acted swiftly to fight the virus and provide medical treatment for patients. It has adopted the most thorough, rigorous and comprehensive prevention and control measures, enforced quarantine and isolation on a scale never seen before, and mobilized medical resources across the country. It has ensured that all those in need have been tested, quarantined, hospitalized or treated. With these measures in place, China has prevented a wider spread and further development of the virus. “The time that can be gained through the full application of these measures [in China] – even if just days or weeks – can be invaluable in ultimately reducing Covid-19 illness and deaths,” says Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) published on February 28, 2020.1
(一)建立统一高效的指挥体系
1.Centralized and Efficient Command
在以习近平同志为核心的中共中央坚强领导下,建立中央统一指挥、统一协调、统一调度,各地方各方面各负其责、协调配合,集中统一、上下协同、运行高效的指挥体系,为打赢疫情防控的人民战争、总体战、阻击战提供了有力保证。
Under the strong leadership of the CPC Central Committee with Xi Jinping at its core, China has put in place an efficient system under which the central authorities exercise overall command, while local authorities and all sectors follow the leadership and instructions of the central authorities, perform their respective duties, and cooperate with each other. This highly efficient system has made it possible for China to win its all-out people’s war against the virus.
习近平总书记亲自指挥、亲自部署。习近平总书记高度重视疫情防控工作,全面加强集中统一领导,强调把人民生命安全和身体健康放在第一位,提出“坚定信心、同舟共济、科学防治、精准施策”的总要求,明确坚决打赢疫情防控的人民战争、总体战、阻击战。习近平总书记主持召开14次中央政治局常委会会议、4次中央政治局会议以及中央全面依法治国委员会会议、中央网络安全和信息化委员会会议、中央全面深化改革委员会会议、中央外事工作委员会会议、党外人士座谈会等会议,听取中央应对疫情工作领导小组和中央指导组汇报,因时因势调整防控策略,对加强疫情防控、开展国际合作等进行全面部署;在北京就社区防控、防疫科研攻关等进行考察,亲临武汉一线视察指导,赴浙江、陕西、山西就统筹推进常态化疫情防控和经济社会发展工作、巩固脱贫攻坚成果进行考察调研;时刻关注疫情动态和防控进展,及时作出决策部署。
General Secretary Xi Jinping takes charge of Covid-19 response.Attaching high importance to Covid-19 prevention and control, Xi Jinping assumed full command over the control efforts from the very beginning. He highlighted the need to put people’s lives and health first, to firm up confidence, strengthen solidarity, adopt a science-based approach, and take targeted measures. He called for a nationwide effort to block the spread of the virus and defeat it. Xi Jinping has chaired 14 meetings of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee, 4 meetings of the Political Bureau, meetings of the Central Commission for Law-based Governance, Central Cyberspace Affairs Commission, Central Commission for Further Reform, and Central Commission for Foreign Affairs, and a meeting with prominent non-CPC figures. At these meetings, he heard briefings from the Central Leading Group for Novel Coronavirus Prevention and Control and the Central Steering Group, adjusted response measures in view of the evolving Covid-19 dynamics, and made decisions on overall plans for strengthening control efforts and international cooperation. He inspected community response and Covid-19 research in Beijing, and visited Wuhan to guide frontline response. He made inspection tours to Zhejiang, Shaanxi and Shanxi provinces where he was briefed on progress in coordinating epidemic prevention and control with economic and social development, and in poverty alleviation. He has closely followed developments in China’s virus control and made timely decisions accordingly.
加强统筹协调、协同联动。中共中央政治局常委、国务院总理、中央应对疫情工作领导小组组长李克强主持召开30余次领导小组会议,研究部署疫情防控和统筹推进经济社会发展的重大问题和重要工作,赴北京、武汉等地和中国疾控中心、中国医学科学院病原生物学研究所、北京西站、首都机场及疫情防控国家重点医疗物资保障调度等平台考察调研。中央指导组指导湖北省、武汉市加强防控工作,以争分夺秒的战时状态开展工作,有力控制了疫情流行,守住了第一道防线。国务院联防联控机制发挥协调作用,持续召开例会跟踪分析研判疫情形势,加强医务人员和医疗物资调度,根据疫情发展变化相应调整防控策略和重点工作。国务院复工复产推进工作机制,加强复工复产统筹指导和协调服务,打通产业链、供应链堵点,增强协同复工复产动能。
Government departments have made well-coordinated control efforts.Premier Li Keqiang, as head of the Central Leading Group for Novel Coronavirus Prevention and Control, has chaired more than 30 meetings of the leading group to discuss key issues concerning Covid-19 control and economic and social development, and important decisions were made at the meetings. He visited Wuhan and inspected China CDC, the Institute of Pathogen Biology CAMS & PUMC, Beijing West Railway Station, Beijing Capital International Airport, and the National Distribution Center for Major Anti-epidemic Medical Supplies. The Central Steering Group responded swiftly to guide Hubei Province and Wuhan City to intensify their control efforts. It thus helped contain the virus and hold a strong first line of defense against the virus. The Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism of the State Council has played the coordinating role and held regular meetings to keep abreast of the situation, dispatch medical teams, and allocate supplies, and it has made timely adjustments to control policies and priorities in response to new developments. Through its mechanism for promoting the return to work, the State Council has strengthened guidance and coordination, removed barriers in the industrial and supply chains, and ensured the resumption of normal daily life.
各地方各方面守土有责、守土尽责。全国各省、市、县成立由党政主要负责人挂帅的应急指挥机制,自上而下构建统一指挥、一线指导、统筹协调的应急决策指挥体系。在中共中央统一领导下,各地方各方面坚决贯彻中央决策部署,有令必行、有禁必止,严格高效落实各项防控措施,全国形成了全面动员、全面部署、全面加强,横向到边、纵向到底的疫情防控局面。
Local authorities and other stakeholders have lived up to their responsibilities. Emergency command mechanisms headed by leading Party and government officials were established in provinces, cities and counties across the country, forming a top-down system with unified command, frontline guidance, and coordination between departments and among provinces. Local authorities and other stakeholders have implemented each and every one of the decisions, plans and prohibitions of the central authorities, and strictly and effectively enforced all response measures. Thus, an effective and well-functioning whole-of-the-nation control mechanism is in place.
(二)构建全民参与严密防控体系
2. A Tight Prevention and Control System Involving All Sectors of Society
针对春节期间人员密集、流动性大的特点,中国迅速开展社会动员、发动全民参与,坚持依法、科学、精准防控,在全国范围内实施史无前例的大规模公共卫生应对举措,通过超常规的社会隔离和灵活、人性化的社会管控措施,构建联防联控、群防群控防控体系,打响抗击疫情人民战争,通过非药物手段有效阻断了病毒传播链条。
The Chinese New Year is marked by enormous population flows in dense groups. In view of this fact, the Chinese government quickly mobilized the whole of society and galvanized the people into a nationwide response. A targeted, law- and science-based approach was adopted, and public health emergency response measures were rolled out on an unprecedented and extensive scale across the country. Through the strictest social distancing and flexible, people-centered social management, China put in place a prevention and control system involving governments at all levels and the whole of society, and launched a people’s war on the virus applying non-medical means that has effectively blocked its transmission routes.
采取有力措施坚决控制传染源。以确诊患者、疑似患者、发热患者、确诊患者的密切接触者等“四类人员”为重点,实行“早发现、早报告、早隔离、早治疗”和“应收尽收、应治尽治、应检尽检、应隔尽隔”的防治方针,最大限度降低传染率。关闭离汉通道期间,武汉对全市421万户居民集中开展两轮拉网式排查,以“不落一户、不漏一人”标准实现“存量清零”,确保没有新的潜在感染源发生。持续提升核酸检测能力,增强试剂盒供应能力,扩充检测机构,缩短检测周期,确保检测质量,实现“应检尽检”“即收即检”。湖北省检测周期从2天缩短到4-6小时,日检测量由疫情初期的300人份提升到4月中旬的5万人份以上,缩短了患者确诊时间,降低了传播风险。在全国范围内排查“四类人员”,以社区网格为基础单元,采取上门排查与自查自报相结合的方式展开地毯式排查。全面实行各类场所体温筛查,强化医疗机构发热门诊病例监测和传染病网络直报,实行2小时网络直报、12小时反馈检测结果、24小时内完成现场流行病学调查,及时发现和报告确诊病例和无症状感染者。加强流行病学追踪调查,精准追踪和切断病毒传播途径,截至5月31日,全国累计追踪管理密切接触者74万余人。
Strong measures were taken to control sources of infection.The Chinese government defined a set of requirements: early detection, reporting, quarantine and treatment with a focus on the four categories of vulnerable people (confirmed cases, suspected cases, febrile patients who might be carriers, and close contacts). It had also taken measures to ensure that they were hospitalized, treated, tested or quarantined as appropriate. It has done everything in its power to reduce infections to the minimum. While keeping all its outbound routes closed, Wuhan carried out two rounds of community-based mass screening of its 4.21 million households, leaving no person or household unchecked and ruling out all potential sources of infection. The Chinese government redoubled efforts to increase the capacity of nucleic acid testing, supply more test kits, and approve more testing institutions. As a result, the testing period was shortened and the quality enhanced, ensuring that all those in need could be tested immediately and as appropriate. In Hubei Province, the testing period was shortened from 2 days to 4-6 hours, and the daily capacity expanded from 300 samples in the early stage of the epidemic to more than 50,000 in mid-April. Such advances made early detection and confirmation of infection possible and reduced the risk of transmission. To identify the four categories of vulnerable people, community grid-based screening was carried out across the country. All residents were requested to report their health condition on a daily basis. Community workers for their part visited households door-to-door to collect and verify this information. Temperature checking was made a routine at all places. Work was done to strengthen the monitoring and online reporting of cases identified at fever clinics of medical facilities – all such cases had to be reported online to higher authorities within 2 hours; their test results sent back to the reporting clinics within 12 hours; and on-site epidemiological investigation completed within 24 hours – so that confirmed cases and asymptomatic carriers would be identified and reported without delay. Epidemiological tracing and investigation were enhanced to precisely detect and cut off virus transmission routes. As of May 31, a total of more than 740,000 close contacts had been traced and handled as appropriate.
第一时间切断病毒传播链。对湖北省、武汉市对外通道实施最严格的封闭和交通管控,暂停武汉及湖北国际客运航班、多地轮渡、长途客运、机场、火车站运营,全国暂停入汉道路水路客运班线发班,武汉市及湖北省多地暂停市内公共交通,阻断疫情向全国以及湖北省内卫生基础设施薄弱的农村地区扩散。对湖北以外地区实施差异化交通管控,湖北省周边省份筑牢环鄂交通管控“隔离带”,防止湖北省疫情外溢蔓延。全国其他地区实行分区分级精准防控,对城乡道路运输服务进行动态管控,加强国内交通卫生检疫。采取有效措施避免人员聚集和交叉感染,延长春节假期,取消或延缓各种人员聚集性活动,各类学校有序推迟开学;关闭影院、剧院、网吧以及健身房等场所;对车站、机场、码头、农贸市场、商场、超市、餐馆、酒店、宾馆等需要开放的公共服务类场所,以及汽车、火车、飞机等密闭交通工具,落实环境卫生整治、消毒、通风、“进出检”、限流等措施,进入人员必须测量体温、佩戴口罩;推行政务服务网上办、预约办,推广无接触快递等“不见面”服务,鼓励民众居家和企业远程办公,有效减少人员流动和聚集;在公共场所设置“一米线”并配以明显标识,避免近距离接触。全国口岸实施严格的出入境卫生检疫,防范疫情通过口岸扩散蔓延。实施最严边境管控,取消非紧急非必要出国出境活动。
Breaking the chains of transmission through early intervention.The strictest closure and traffic restrictions were enforced on all outbound routes from Wuhan and Hubei. International passenger flights, and ferries and long-distance passenger transport services in many parts of the province were suspended, as were road and waterway passenger services bound for Wuhan from other places of the country. Airports and railway stations were closed and intra-city public transport halted in Wuhan and many other parts of Hubei. All these restrictions effectively stopped the virus from spreading nationwide, especially in rural Hubei where public health infrastructure was relatively weak.
Areas outside Hubei took a differentiated approach to traffic control. The provinces abutting Hubei built traffic control “isolation zones” around the province, preventing the virus from spreading beyond Hubei. Other parts of China adopted a targeted, tiered, and region-specific approach. They exercised a dynamic control over urban and rural road transport services and strengthened health and quarantine measures for domestic routes.
Rigorous measures were taken to prevent public gatherings and cross-infection. The Chinese New Year holiday was extended, public gatherings were canceled or postponed, and the spring semester was postponed in schools. Cinemas, theaters, internet cafés, and gyms were all closed. Strict procedures had to be followed in essential public facilities, including bus stations, airports, ports, farmers markets, shopping malls, supermarkets, restaurants and hotels, and in enclosed transport vehicles such as buses, trains and planes. All persons were required to wear masks and undergo temperature monitoring when accessing these venues or vehicles. In addition, all such facilities had to be disinfected, meet certain hygiene standards, ensure good ventilation, monitor visitors’ temperature, and control the number of passengers or visitors at a given period of time. Government services were provided online and through prior reservation, non-physical-contact delivery or services were extended, people were encouraged to stay at home and work from home, and businesses were encouraged to telecommute – all these measures effectively reduced population flows and public gatherings. Clear signs urging people to maintain at least one meter of distance and avoid close contact could be seen in all public places. Strict health and quarantine measures were enforced at points of entry and exit across China to prevent inbound and outbound spread of the virus. The strictest-ever measures were applied at border control to suspend non-urgent and nonessential outbound travel by Chinese citizens.
牢牢守住社区基础防线。城乡社区是疫情联防联控的第一线,是外防输入、内防扩散的关键防线。充分发挥基层主体作用,加强群众自治,实施社区封闭式、网格化管理,把防控力量、资源、措施向社区下沉,组建专兼结合工作队伍,充分发挥街道(乡镇)和社区(村)干部、基层医疗卫生机构医务人员、家庭医生团队作用,将一个个社区、村庄打造成为严密安全的“抗疫堡垒”,把防控有效落实到终端和末梢。按照“追踪到人、登记在册、社区管理、上门观察、规范运转、异常就医”的原则,依法对重点人群进行有效管理,开展主动追踪、人员管理、环境整治和健康教育。武汉市全面实施社区24小时封闭管理,除就医和防疫相关活动外一律禁止出入,由社区承担居民生活保障。其他地方对城市社区、农村村落普遍实施封闭式管理,人员出入检查登记、测量体温。加强居民个人防护,广泛开展社会宣传,强化个体责任意识,自觉落实居家隔离以及跨地区旅行后隔离14天等防控要求,严格执行外出佩戴口罩、保持社交距离、减少聚集等防护措施,养成勤洗手、常通风等良好生活习惯。大力开展爱国卫生运动,提倡文明健康、绿色环保的生活方式。
The community-based line of defense was well guarded. Communities and villages made up the first line of defense in epidemic prevention and control, a major barrier to inbound cases and local transmission. They served as the mainstay in China’s Covid-19 response. Residents and villagers were mobilized to help manage communities. Strict access control and grid-based management were exercised in communities, and human and material resources were channeled down to the community level to reinforce implementation of targeted measures. Task forces comprising both full-time and part-time community workers were set up, while officials at the sub-district/township and community/village levels, health workers of community medical facilities, and family doctors all performed their duties as a team. Through all these efforts, communities and villages were turned into strongholds, securing full implementation of response measures down to the lowest level. To deal with the four categories of vulnerable people, a number of measures were taken in accordance with the law, such as tracing, registering, and visiting each individual, placing them under community management, and transferring them, if necessary, to designated medical facilities for quarantine or treatment as per due procedures. Community actions were taken to keep local areas in good condition and promote health education. In Wuhan, rigorous 24-hour access control was enforced in all residential communities. No residents were allowed to leave and no non-residents allowed to access the community area other than for essential medical needs or epidemic control operations. Community workers were responsible for the purchase and delivery of daily necessities according to residents’ needs. This approach was also applied in communities and villages in other parts of China, where all residents had to register and undergo temperature checking when leaving or entering the residential area or village. Education programs were conducted to raise public awareness of the need for personal protection and enhance the sense of social responsibility. People observed self-quarantine at home and 14-day self-isolation after cross-region travel. They strictly followed personal protection measures such as wearing a mask when going out, maintaining proper social distancing, avoiding crowds, frequent handwashing, and regular ventilation. The tradition of the Patriotic Public Health Campaign which was initiated in the 1950s, with an emphasis on sanitation and personal hygiene, was also encouraged, along with a healthy, environment-friendly lifestyle .
实施分级、分类、动态精准防控。全国推行分区分级精准施策防控策略,以县域为单位,依据人口、发病情况综合研判,划分低、中、高疫情风险等级,分区分级实施差异化防控,并根据疫情形势及时动态调整名单,采取对应防控措施。低风险区严防输入,全面恢复生产生活秩序;中风险区外防输入、内防扩散,尽快全面恢复生产生活秩序;高风险区内防扩散、外防输出、严格管控,集中精力抓疫情防控。本土疫情形势稳定后,以省域为单元在疫情防控常态化条件下加快恢复生产生活秩序,健全及时发现、快速处置、精准管控、有效救治的常态化防控机制。全力做好北京市疫情防控,确保首都安全。做好重点场所、重点单位、重点人群聚集性疫情防控和处置,加强老年人、儿童、孕产妇、学生、医务人员等重点人群健康管理,加强医疗机构、社区、办公场所、商场超市、客运场站、交通运输工具,托幼机构、中小学校、大专院校以及养老机构、福利院、精神卫生医疗机构、救助站等特殊场所的管控,覆盖全人群、全场所、全社区,不留死角、不留空白、不留隐患。针对输入性疫情,严格落实国境卫生检疫措施,强化从“国门”到“家门”的全链条、闭环式管理,持续抓紧抓实抓细外防输入、内防反弹工作。
A multi-level, category-specific, dynamic and targeted approach was adopted.China also applied a region-specific, multi-level approach to epidemic prevention and control. To better prevent and control the epidemic, each region at or above the county level was classified by risk level on the basis of a comprehensive evaluation of factors such as population and number of infections in a given period of time. There are three levels of risk: low, medium, and high. Regions could take measures according to the risk level, which was dynamic and adjusted in light of the evolving situation.
In response to Covid-19, a low-risk region was requested to remain vigilant against any potential inbound transmission while fully restoring normal order in work and daily life; a medium-risk region had to prevent inbound and local transmission while restoring normal work and daily life as soon as possible; and a region classified as high-risk was obliged to prevent any spread in its jurisdiction or beyond, enforce strict control measures, and focus on containment. Once the situation stabilized, provincial-level authorities could step up efforts to restore order in work and daily life in areas under their jurisdiction, while adapting to the new normal of Covid-19 control by establishing a sound long-term epidemic response system that ensures early detection, quick response, targeted prevention and control, and effective treatment. Every effort has been made to stem the virus spread in the capital of Beijing to safeguard public health.
Appropriate measures were implemented to prevent any cluster outbreaks in key locations, major organizations, and priority population groups, and manage the aftermath of any such outbreaks. The elderly, children, pregnant women, students, and health workers were to be well protected as a priority.
Health management of priority population groups was enhanced. Protective measures were intensified in medical facilities, communities, office buildings, shopping malls and supermarkets, passenger terminals, transport vehicles, child-care centers and kindergartens, elementary and secondary schools, colleges and universities, nursing homes, charity houses, mental health institutions, and first-aid stations. These measures were implemented nationwide, covering all population groups, locations, and communities, and leaving no areas unattended and no hidden dangers unaddressed.
To control any inbound infections from overseas, China has strictly enforced its border health and quarantine rules to ensure a full, closed cycle of management of all arrivals, from their entry at the border to the doorstep of where they would stay. Sustained, meticulous efforts have been made to prevent both inbound cases and a recurrence in domestic cases.
为疫情防控提供有力法治保障。依法将新冠肺炎纳入《中华人民共和国传染病防治法》规定的乙类传染病并采取甲类传染病的预防、控制措施,纳入《中华人民共和国国境卫生检疫法》规定的检疫传染病管理,同时做好国际国内法律衔接。一些地方人大常委会紧急立法,在国家法律和法规框架下授权地方政府在医疗卫生、防疫管理等方面,规定临时性应急行政管理措施。严格执行传染病防治法及其实施办法等法律法规,出台依法防控疫情、依法惩治违法犯罪、保障人民生命健康安全的意见,加强治安管理、市场监管,依法惩处哄抬物价、囤积居奇、制假售假等破坏疫情防控的违法犯罪行为,强化防疫物资质量和价格监管,加大打击虚假违法广告力度,保障社会稳定有序。加强疫情防控期间行政执法监督,严格规范执法,公正文明执法,依法化解与疫情相关的法律纠纷,为疫情防控和企业复工复产提供法律保障和服务。加强普法宣传,引导公众依法行事。
Legal safeguards for epidemic prevention and control were strengthened. China listed Covid-19 as a Class B infectious disease, but addressed it with measures applicable to a Class A infectious disease under the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases. It also applied control and quarantine measures under the Frontier Health and Quarantine Law of the People’s Republic of China consistent with relevant provisions of international law and other domestic laws. Standing committees of some sub-national people’s congresses launched emergency legislation procedures as per the national legal framework, empowering local governments to introduce interim emergency administrative rules relating to healthcare and epidemic control. The Law on Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases and measures for its implementation have been strictly enforced, and guidelines have been promulgated on controlling the disease, combating epidemic-related crimes in accordance with the law, and protecting people’s lives and health. Law and order, and market supervision have been strengthened. Price gouging, hoarding and profiteering, production and sales of counterfeit or sub-standard products, and any other crimes impeding response efforts have been punished by law. Quality and price control of anti-epidemic supplies has been reinforced, and stronger measures have been taken against deceptive and illegal advertising, ensuring social order and stability. Supervision on administrative law enforcement has been intensified during epidemic control to ensure that the law is enforced in a strict, impartial, procedure-based, and non-abusive way. Legal disputes associated with the epidemic have been resolved in accordance with the law, and legal guarantees and services have been provided for Covid-19 response and for businesses returning to work. The government has also made greater efforts to raise public legal awareness and guide people to act within the parameters of the law.
遵循科学规律开展防控。新冠病毒是新病毒,对其认识需要有个过程。积极借鉴以往经验,紧密结合中国国情,遵循流行病学规律,探索行之有效的方法手段,用中国办法破解疫情防控难题。注重发挥病毒学、流行病学、临床医学等领域专家作用,及时开展疫情形势分析研判,提出防控策略建议,充分尊重专家意见,增强疫情防控的科学性专业性。秉持科学态度,加强病毒感染、致病机理、传播途径、传播能力等研究,与世界卫生组织及其他国家和地区保持沟通交流。随着对病毒认识的不断深化,及时调整和优化工作措施,不断提升防控水平。根据疫情形势变化和评估结果,先后制修订6版新冠肺炎防控方案,科学规范开展病例监测、流行病学调查、可疑暴露者和密切接触者管理以及实验室检测等工作。针对重点人群、重点场所、重点单位发布15项防控技术方案、6项心理疏导工作方案,并细化形成50项防控技术指南,进一步提高疫情防控的科学性精准性。
Prevention and control efforts have been based on science.Covid-19 is a new virus and it will take time for humanity to understand it completely. In its quest for victory over the coronavirus, China has been mapping its own route to success – one based on reliable experience, tailored to its national conditions, and rooted in sound epidemiological practice. China values the role of experts in virology, epidemiology, clinical medicine and related fields. China’s response has been professional because its response measures were based on timely analyses and assessments by scientists and public health experts, whose views and proposals were fully respected. China has given full support to factual and scientific research on virus infection, pathogenesis, transmission routes and transmissibility while maintaining exchanges and communication with the WHO and other countries and regions. With a growing body of knowledge of the virus, China has modified and optimized its response measures in a timely manner to make them more effective. It has developed a Covid-19 prevention and control protocol and updated it five times based on assessments of the evolving epidemic dynamics. The protocol provides a set of reliable standards for case monitoring, epidemiological investigation, management of close contacts and of those suspected of exposure to infection, and procedure-based tests in laboratories. China has also published 15 technical manuals on epidemic prevention and control for key population groups, locations and organizations, 6 work plans on psychological counseling for people affected by Covid-19, and 50 specific technical guidelines. All of this has ensured that China’s prevention and control efforts are more targeted and science-based.
(三)全力救治患者、拯救生命
3.An All-Out Effort to Treat Patients and Save Lives
医疗救治始终以提高收治率和治愈率、降低感染率和病亡率的“两提高”“两降低”为目标,坚持集中患者、集中专家、集中资源、集中救治“四集中”原则,坚持中西医结合,实施分类救治、分级管理。对重症患者,调集最优秀的医生、最先进的设备、最急需的资源,不惜一切代价进行救治,大幅度降低病亡率;对轻症患者及早干预,尽可能在初期得以治愈,大幅度降低转重率。
From the outset, China’s goal in its medical response to Covid-19 has been to improve the patient admission and cure rates and reduce the infection and fatality rates. The infected were treated in dedicated medical facilities where medical specialists from all over the country and all the necessary medical resources were concentrated. Both traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine were applied. A condition-specific and category-based approach was applied to medical treatment of patients. Severe cases were treated by the best doctors using the most advanced equipment, and critical supplies were pooled to save lives at all costs. It is through such efforts that the Covid-19 fatality rate in China has dropped sharply. Early medical intervention has made it possible to have patients with mild symptoms cured without delay, thus significantly reducing the risk that their condition might worsen.
集中优势资源加强重症救治。疫情突发导致武汉市医疗资源挤兑。针对疫情初期患者数量激增与床位资源不足的突出矛盾,集中资源和力量在武汉市建设扩充重症定点医院和救治床位,将全部重症危重症患者集中到综合实力最强且具备呼吸道传染性疾病收治条件的综合医院集中开展救治。建成火神山、雷神山两座各可容纳1000多张床位的传染病专科医院,改扩建一批定点医院,改造一批综合医院,使重症床位从1000张左右迅速增加至9100多张,解决了重症患者大规模收治难题。优化重症救治策略,制定个体化医疗救治方案。建立专家巡查制度,定期组织专家团队对武汉市定点医院重症患者救治进行巡诊,评估患者病情和治疗方案。针对超过80%的重症患者合并严重基础性疾病情况,实行“一人一策”,建立感染、呼吸、重症、心脏、肾脏等多学科会诊制度,并制定重症、危重症护理规范,推出高流量吸氧、无创和有创机械通气、俯卧位通气等措施。严格落实疑难危重症患者会诊制度、死亡病例讨论制度等医疗质量安全核心制度,强化对治愈出院患者健康监测,确保重症患者救治质量。开展康复者恢复期血浆采集和临床治疗工作,建立应急储备库,截至5月31日,全国共采集恢复期血浆2765人次,1689人次患者接受恢复期血浆治疗,取得较好治疗效果。
Pooling premium resources to treat severe cases. The sudden appearance of Covid-19 in Wuhan put an overwhelming strain on its medical resources. There was a severe shortage of hospital beds in the early stage as the number of infections surged. By directing resources to Wuhan, China expanded the capacity of designated hospitals to deal with severe cases and increased the number of beds. Patients in severe and critical condition were gathered for treatment and intensive care at the best hospitals with the greatest capacity for accommodating patients with infectious respiratory diseases. Two hospitals with 1,000-plus beds each – Huoshenshan and Leishenshan – were built as specialist hospitals for treating infectious diseases, and a number of designated and general hospitals were expanded or remodeled. The number of beds for severe cases quickly increased from around 1,000 to more than 9,100. Hospitals were able to admit large numbers of patients who were seriously ill.
The treatment strategy for severe cases was improved, and tailored treatment provided to individual patients. Inspection teams consisting of top experts were organized to regularly inspect Wuhan’s designated hospitals and evaluate patients in critical condition and their therapeutic regimen. For those with serious underlying medical conditions, who accounted for more than 80 percent of all severe cases, case-by-case treatment was prescribed after consultation with a multidisciplinary team consisting of experts on infection, respiratory diseases, heart and kidney diseases, and intensive care. In addition, a set of standards were formulated for nursing patients in severe and critical condition, and such measures as high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy, non-invasive and invasive mechanical ventilation, and ventilation in a prone position were adopted. Expert consultation on complex, severe and critical cases, and fatal cases, and other core medical security systems were strictly implemented. Those who have been cured and discharged from hospital have received rigorous health monitoring, and patients in severe condition have been given quality medical treatment. The plasma of convalescent Covid-19 patients has been collected to set up an emergency plasma reserve, and convalescent plasma therapy has been applied in clinical treatment. As of May 31, convalescent plasma had been collected from 2,765 recovered patients, and 1,689 patients had been treated with the therapy, with positive results.
对轻症患者及早干预治疗。及时收治轻症患者,及早实施医疗干预,尽量减少轻症转为重症。完善临床救治体系,全国共指定1万余家定点医院,对新冠肺炎患者实行定点集中治疗。建立全国医疗救治协作网络,通过远程会诊方式提供技术支持。武汉市针对患者数量急剧增长、80%左右是轻症的情况,集中力量将一批体育场馆、会展中心等改造成16家方舱医院,床位达到1.4万余张,使轻症患者应收尽收、应治尽治,减少了社区感染传播,减少了轻症向重症转化。16家方舱医院累计收治患者1.2万余人,累计治愈出院8000余人、转院3500余人,实现“零感染、零死亡、零回头”。方舱医院是阻击重大传染病的重大创新,使“应收尽收”“床位等人”成为现实,有力扭转了防控形势。英国《柳叶刀》社论认为,“中国建造的方舱庇护医院对于缓解医疗卫生系统所承受的巨大压力有着至关重要的作用”。(注2)
Early intervention for patients with mild symptoms.China has been quick to have patients with mild symptoms admitted to designated medical facilities for early medical intervention, and has done its best to prevent mild cases from worsening. The national clinical treatment network has been expanded to include more than 10,000 hospitals dedicated to the treatment of Covid-19 patients. A national network of medical treatment coordination has also been formed to provide technical support through online consultation. In Wuhan, faced with surging infections and considering that 80 percent of cases were mild, the city government mobilized resources to repurpose stadiums and exhibition centers into 16 temporary treatment centers. With some 14,000 beds, these centers were able to admit all confirmed mild cases for treatment. This helped to reduce infections and virus transmission in communities and prevent mild cases from worsening. The 16 treatment centers received a total of more than 12,000 patients; 8,000 and more were cured and discharged; and more than 3,500 were transferred to hospitals. While in service, these facilities had zero cases of infection, death, or relapse.
Temporary treatment centers, or Fangcang shelter hospitals, are a major innovative solution that provided enough beds to admit all confirmed cases, thus turning the tide in the battle against Covid-19. An article in The Lancet wrote, “To relieve the huge pressure on the healthcare system, Fangcang shelter hospitals have also been crucial.”2
及时总结推广行之有效的诊疗方案。坚持边实践、边研究、边探索、边总结、边完善,在基于科学认知和证据积累的基础上,将行之有效的诊疗技术和科技研究成果纳入诊疗方案。先后制修订7版新冠肺炎诊疗方案,3版重型、危重型病例诊疗方案,2版轻型、普通型管理规范,2版康复者恢复期血浆治疗方案,1版新冠肺炎出院患者主要功能障碍康复治疗方案,提高了医疗救治工作的科学性和规范性。最新的第7版新冠肺炎诊疗方案增加病理改变内容,增补和调整临床表现、诊断标准、治疗方法和出院标准等,并纳入无症状感染者可能具有感染性、康复者恢复期血浆治疗等新发现。目前,第7版诊疗方案已被多个国家借鉴和采用。强化治愈出院患者隔离管理和健康监测,加强复诊复检和康复,实现治疗、康复和健康监测一体化全方位医疗服务。注重孕产妇、儿童等患者差异性诊疗策略,实现不同人群诊疗方案的全覆盖。
Reviewing diagnostic and therapeutic plans and applying effective ones on a broad scale.China’s diagnostic and therapeutic plans for Covid-19 have been developed and improved through clinical practice, medical research, experimentation and regular reviews. Based on scientific knowledge and accumulated evidence, R&D results and the diagnostic and therapeutic regimens that proved effective were incorporated in the national diagnosis and treatment plans. These include seven versions of the diagnosis and treatment protocol, three editions of the protocol for severe and critical cases, two editions of the manual for mild case management, two editions of convalescent plasma therapy treatment protocol, and one rehabilitation treatment program for patients discharged from hospitals. All these protocols and plans have contributed to science-based treatment of patients and the establishment of standards for medical treatment.
In Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Covid-19 (Trial Version 7), information on pathological changes, clinical symptoms, criteria for diagnosis, therapies, and criteria for patient discharge was added or updated. The protocol states that asymptomatic cases may be contagious. It also notes that plasma from convalescent cases may work in treating the infected. This edition has been adopted or used for reference in a number of countries. Concerning discharged patients, quarantining, monitoring of their health and rehabilitation, and reexamination and re-testing have all been strengthened. Integrated medical services covering treatment, rehabilitation and health monitoring have been put in place. Differentiated treatment approaches have been adopted for children and pregnant women, among other groups.
充分发挥中医药特色优势。坚持中西医结合、中西药并用,发挥中医药治未病、辨证施治、多靶点干预的独特优势,全程参与深度介入疫情防控,从中医角度研究确定病因病基、治则治法,形成了覆盖医学观察期、轻型、普通型、重型、危重型、恢复期发病全过程的中医诊疗规范和技术方案,在全国范围内全面推广使用。中医医院、中医团队参与救治,中医医疗队整建制接管定点医院若干重症病区和方舱医院,其他方舱医院派驻中医专家。中医药早期介入、全程参与、分类救治,对轻症患者实施中医药早介入早使用;对重症和危重症患者实行中西医结合;对医学观察发热病人和密切接触者服用中药提高免疫力;对出院患者实施中医康复方案,建立全国新冠肺炎康复协作网络,提供康复指导。中医药参与救治确诊病例的占比达到92%。湖北省确诊病例中医药使用率和总有效率超过90%。筛选金花清感颗粒、连花清瘟胶囊/颗粒、血必净注射液和清肺排毒汤、化湿败毒方、宣肺败毒方等“三药三方”为代表的针对不同类型新冠肺炎的治疗中成药和方药,临床疗效确切,有效降低了发病率、转重率、病亡率,促进了核酸转阴,提高了治愈率,加快了恢复期康复。
Leveraging the unique strength of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).Both TCM and Western medicine were used and traditional Chinese and Western drugs administered. China has leveraged the unique strength of TCM in preemptive prevention, differentiated medication, and multi-targeted intervention, and at every step of Covid-19 treatment and control. The etiology and pathogen of the disease were analyzed and confirmed through TCM methodology, as were the principles and methods of treatment. A set of TCM diagnosis and treatment protocols were developed to cover the entire process of medical observation, treatment of mild, moderate, severe, and critical cases, and recovery, and they have been applied nationwide.
TCM hospitals were used in the treatment of Covid-19 patients, and TCM teams took charge of and ran some wards for patients in severe condition at designated hospitals and some treatment centers. All the other shelter hospitals had resident TCM experts. TCM has played its part in the entire process of Covid-19 response, from early intervention to administering case-specific treatment. TCM drugs and treatment methods were used for early intervention and treatment of patients with mild symptoms; for patients with severe symptoms they were used in combination with Western medicine; for those under medical observation for fever and those who had been in close contact with confirmed cases they served to improve immunity; they helped to strengthen the constitution of those who had recovered. A national TCM coordination network was formed to offer guidance to patients recovering from the disease. Chinese herbal formulas and drugs were administered to 92 percent of all confirmed cases. In Hubei Province, more than 90 percent of confirmed cases received TCM treatment that proved effective. Jinhua Qinggan Granules, Lianhua Qingwen Capsules/Granules, Xuebijing Injection, Lung Cleansing and Detoxifying Preparation, Dampness Resolving and Detoxifying Preparation, Lung Diffusing and Detoxifying Preparation, and other TCM drugs and herbal formulas have proved effective in treating different types of Covid-19 patients. They have significantly reduced the incidence rate, prevented cases with mild symptoms from worsening, increased the cure rate, lowered the fatality rate, helped nucleic acid turn negative, and sped up the rehabilitation of recovered Covid-19 patients.
实施患者免费救治。及时预拨疫情防控资金,确保患者不因费用问题影响就医,确保各地不因资金问题影响医疗救治和疫情防控。截至5月31日,全国各级财政共安排疫情防控资金1624亿元。及时调整医保政策,明确确诊和疑似患者医疗保障政策,对确诊和疑似患者实行“先救治,后结算”。对新冠肺炎患者(包括确诊和疑似患者)发生的医疗费用,在基本医保、大病保险、医疗救助等按规定支付后,个人负担部分由财政给予补助。异地就医医保支付的费用由就医地医保部门先行垫付。截至5月31日,全国确诊住院患者结算人数5.8万人次,总医疗费用13.5亿元,确诊患者人均医疗费用约2.3万元。其中,重症患者人均治疗费用超过15万元,一些危重症患者治疗费用几十万元甚至上百万元,全部由国家承担。
Providing free treatment for patients. Government funds for Covid-19 control were made available in advance to ensure that patients could receive timely treatment and local authorities could proceed smoothly with measures for medical treatment and epidemic control. As of May 31, a total of RMB162.4 billion had been allocated by governments of all levels to fight the virus.
Policies for medical insurance were quickly adjusted, with clear provisions for confirmed or suspected Covid-19 patients. They could get treatment with delayed settlement of accounts. All Covid-19 patients, confirmed or suspected, received subsidies from state finance for any medical bills not covered by basic medical insurance, serious disease insurance, or the medical assistance fund. In the case of patients receiving treatment in places where they were not registered for basic medical insurance, their medical bills related to Covid-19 were paid by the local insurance fund first and settled later.
As of May 31, the medical bills of 58,000 inpatients with confirmed infections had been settled by basic medical insurance, with a total expenditure of RMB1.35 billion, or RMB23,000 per person. The average cost for treating Covid-19 patients in severe condition surpassed RMB150,000, and in some critical cases the individual cost exceeded RMB1 million, all covered by the state.
加强医疗机构感染控制和医务人员防护。制定感染控制技术指南和制度文件,明确医疗机构重点区域、就诊流程“三区两通道”建筑布局要求。加强对医务人员的感染控制培训,开展全国督导,确保感染控制措施落实。对疫情严重、院内感染风险高、医疗救治压力大的重点地区重点医院,有针对性地开展指导。加强医疗废物分类收集、运送贮存,做好病亡者遗体处置。在援鄂援汉医疗队中配置感染控制专家,全国支援湖北省和武汉市的医务人员没有感染病例。2月份以后,全国医务人员感染病例报告数明显减少。关心关爱医务人员,制定一系列保障政策,开展心理疏导,妥善安排轮换休整,缓解身体和心理压力,保持一线医务人员战斗力。
Strengthening infection control at medical institutions and ensuring personal protection for health workers. A set of technical manuals and normative documents on infection control were developed to regulate the layout of key areas in medical institutions and the consultation and treatment process, including clean zones, partially contaminated zones, contaminated zones, and separate passages for medical staff and patients. Health workers received training in workplace infection control, and nationwide supervision was strengthened to ensure control measures were implemented to the letter. Targeted guidance was given to the hardest-hit areas, hospitals at a higher risk of infection among staff, and areas and hospitals under the greatest pressure in treating patients. A major effort was put into the sorting, collection, storage and removal of medical waste, and the treatment of the remains of the deceased. All emergency medical teams coming to Wuhan and Hubei from other parts of China had at least one infection control expert. Thanks to this arrangement, there have been no cases of infection in the teams. Since February there has been a sharp drop in the number of reported infections among medical staff nationwide. Health workers have been cared for and their needs attended to. A series of policies and measures have been introduced to ensure their wellbeing, such as psychological counseling and staff rotation, to ease their physical and psychological stress, help them stay healthy, and allow them to continue the fight on the front line.
(四)依法及时公开透明发布疫情信息
4.China Has Released Information in an Open and Transparent Manner as Required by Law
在全力做好疫情防控的同时,中国以对生命负责、对人民负责、对历史负责、对国际社会负责的态度,建立最严格且专业高效的信息发布制度,第一时间发布权威信息,速度、密度、力度前所未有。持续、权威、清晰的疫情信息,有效回应了公众关切、凝聚了社会共识,为其他国家提供了参考和借鉴。
While making an all-out effort to contain the virus, China has also acted with a keen sense of responsibility to humanity, its people, posterity, and the international community. It has provided information on Covid-19 in a thoroughly professional and efficient way. It has released authoritative and detailed information as early as possible on a regular basis, thus effectively responding to public concern and building public consensus. Its experience is something other countries can draw on in their fight against the virus.
建立严格的疫情发布机制。依法、及时、公开、透明发布疫情信息,制定严格规定,坚决防止瞒报、迟报、漏报。武汉市从2019年12月31日起依法发布疫情信息,并逐步增加信息发布频次。2020年1月21日起,国家卫生健康委每日在官方网站、政务新媒体平台发布前一天全国疫情信息,各省级卫生健康部门每日统一发布前一天本省份疫情信息。2月3日起,国家卫生健康委英文网站同步发布相关数据。
A strict system of information release has been established. China has released information on Covid-19 in a timely, open and transparent manner as required by law. Strict regulations are in place to see there is no withholding of information, underreporting, or delay in reporting cases of infection. On December 31, 2019, the Wuhan government began to release coronavirus information in accordance with the law, and gradually increased the frequency of release. Since January 21, 2020, the NHC has provided daily updates on nationwide cases on its official website and social media platform, and provincial health departments have done the same on local cases. Starting from February 3, the NHC has released the information simultaneously on its English-language website.
建立分级分层新闻发布制度。坚持国家和地方相结合、现场发布与网上发布相结合,建立多层次多渠道多平台信息发布机制,持续发布权威信息,及时回应国内外关注的疫情形势、疫情防控、医疗救治、科研攻关等热点问题。截至5月31日,国务院联防联控机制、国务院新闻办公室共举行新闻发布会161场,邀请50多个部门490余人次出席发布会,回答中外媒体1400多个提问;湖北省举行103场新闻发布会,其他省份共举行1050场新闻发布会。
A tiered news release mechanism has been formed. At both national and local levels, a tiered information release mechanism has been formed to circulate authoritative information through various channels and platforms, both onsite and online, in order to address domestic and international concerns on virus control, medical treatment, and scientific research. By May 31, the Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism and the Information Office of the State Council had held 161 press conferences during which officials from more than 50 government departments appeared over 490 times and answered more than 1,400 questions from Chinese and foreign media. One hundred and three press conferences had been held in Hubei and 1,050 in the other provinces.
依法适时订正病例数据。本土疫情得到控制后,为确保公开透明、数据准确,武汉市针对疫情早期因收治能力不足导致患者在家中病亡、医院超负荷运转、死亡病例信息登记不全等原因,客观上存在迟报、漏报、误报现象,根据相关法律规定,在深入开展涉疫大数据与流行病学调查的基础上,对确诊和死亡病例数进行了订正,并向社会公开发布。
Covid-19 statistics have been updated in accordance with the law. In the early stage of Covid-19 control, there were late, incomplete and erroneous reports of Covid-19 cases in Wuhan due to unverified deaths at home, inadequate hospital capacity, hospitals being overwhelmed, and incomplete recording of deaths. After the domestic spread of Covid-19 had been brought under control, the city updated the number of confirmed cases and deaths based on big data application and an epidemiological investigation to ensure accuracy of the data, and released the results in an open and transparent manner in accordance with the law.
多渠道多平台传播信息。国家卫生健康委中、英文官方网站和政务新媒体平台设置疫情防控专题页面,发布每日疫情信息,解读政策措施,介绍中国抗疫进展,普及科学防控知识,澄清谣言传言。各省(自治区、直辖市)政府网站及政务新媒体平台及时发布本地疫情信息和防控举措。大力开展应急科普,通过科普专业平台、媒体和互联网面向公众普及科学认知、科学防治知识,组织权威专家介绍日常防控常识,引导公众理性认识新冠肺炎疫情,做好个人防护,消除恐慌恐惧。加强社会舆论引导,各类媒体充分传递抗击疫情正能量,同时发挥舆论监督作用,推动解决疫情防控中出现的问题。
Covid-19-related information is provided through various channels and platforms. The NHC’s official Chinese and English websites and its social media platform have special sections where Covid-19-related information is released on a daily basis, including information on relevant policies, progress in China’s containment efforts, updates on disease prevention and control, and clarifications that refute rumors. Information on local Covid-19 control has been promptly released on government websites and social media platforms of all provinces. To disseminate knowledge about its Covid-19 response, China has released relevant information through platforms for popularizing science, and through the media and the internet. Leading medical experts have offered advice on routine self-protection to help the public see Covid-19 in a rational way and forestall panic. The media has expanded public outreach and sent a positive message in combating the virus, and public opinion has played its role of oversight to help solve problems affecting virus control.
(五)充分发挥科技支撑作用
5.Science and Technology Underpin China’s Efforts
科学技术是人类同疾病较量的锐利武器,人类战胜大灾大疫离不开科学发展和技术创新。面对人类未知的新冠病毒,中国坚持以科学为先导,充分运用近年来科技创新成果,组织协调全国优势科研力量,以武汉市为主战场,统筹全国和疫情重灾区,根据疫情发展不同阶段确定科研攻关重点,坚持科研、临床、防控一线相互协同和产学研各方紧密配合,为疫情防控提供了有力科技支撑。
Science and technology are the sharp blade that humanity wields in the battle against disease. Such battles could not have been won without scientific advances and technological innovation. Confronted by Covid-19, a previously unknown virus, China has exploited the pioneering role of science and technology and fully applied the results of scientific and technical innovation in recent years. Top scientific research resources have gathered from around the nation to support virus control. Focusing on the main battlefield of Wuhan and coordinating efforts in the most severely-affected areas and across the rest of the country, China pinpointed key R&D areas for different stages of virus control. The close coordination between scientific research, clinical application, and frontline virus control, and between enterprises, universities, and research institutes, has given powerful support for the war against the virus.
实施科研应急攻关。遵循安全、有效、可供的原则,加快推进药物、疫苗、新型检测试剂等研发和应用。适应疫情防控一线的紧迫需求,围绕“可溯、可诊、可治、可防、可控”,坚持产学研用相结合,聚焦临床救治和药物、疫苗研发、检测技术和产品、病毒病原学和流行病学、动物模型构建5大主攻方向,组织全国优势力量开展疫情防控科技攻关,加速推进科技研发和应用,部署启动83个应急攻关项目。按照灭活疫苗、重组蛋白疫苗、减毒流感病毒载体疫苗、腺病毒载体疫苗、核酸疫苗等5条技术路线开展疫苗研发。目前,已有4种灭活疫苗和1种腺病毒载体疫苗获批开展临床试验,总体研发进度与国外持平,部分技术路线进展处于国际领先。组织科研团队开展科学溯源研究。
Key progress has been made in scientific research. Following the principles of safety, effectiveness and availability, China has accelerated the R&D and application of medicines, vaccines, and new test kits. To meet the urgent needs of frontline virus control, and to ensure traceability of infection sources, diagnosis and treatment of patients, and prevention and control of infections, China has pooled resources from enterprises, universities, and research institutes, directing them to focus on five areas – clinical treatment, new medicines and vaccines, testing techniques and products, viral etiology and epidemiology, and animal model construction. Top research resources from around the nation have been galvanized to work on these tasks in pursuit of early results and application. A total of 83 emergency R&D programs have been initiated. Vaccines are being developed in five categories – inactivated vaccines, recombinant protein vaccines, live attenuated influenza vaccines, adenovirus vaccines, and nucleic acid-based vaccines. To date, four inactivated vaccines and one adenovirus vaccine have been approved for clinical trials. While scientists in China and abroad have kept up with mutual developments, China leads the world in the development of certain types of vaccines. Research teams have also been assembled to trace the origin of Covid-19.
坚持科研攻关和临床救治、防控实践相结合。第一时间研发出核酸检测试剂盒,推出一批灵敏度高、操作便捷的检测设备和试剂,检测试剂研发布局涵盖核酸检测、基因测序、免疫法检测等多个技术路径。坚持“老药新用”基本思路,积极筛选有效治疗药物,探索新的治疗手段,在严谨的体外研究和机制研究基础上,不断总结救治经验,推动磷酸氯喹、恢复期血浆、托珠单抗和中医药方剂、中成药等10种药物或治疗手段进入诊疗方案,获得4项临床批件,形成5项指导意见或专家共识。开展试验性临床治疗,加快推广应用临床验证有效的诊疗方法和药物。强化实验室生物安全监管,加强新冠病毒临床检测血液样本和实验室检测生物样本管理。
Scientific R&D has been integrated with clinical treatment and epidemic control. Having promptly developed nucleic acid test kits, China has also introduced a range of high-sensitivity, easy-to-use test equipment and reagents. Its R&D of reagents covers nucleic acid testing, gene testing, and immunological testing. Putting existing medicines to new use, China has searched for effective medicines and new therapies, and summarized clinical experience based on rigorous in vitro experiments and pathogenic research. Ten types of medicine, including chloroquine phosphate, tocilizumab, finished TCM drugs, and herbal preparations, as well as convalescent plasma therapy, have been adopted in treatment plans. Approval for clinical trial has been given to four medicines, and guidelines formed or expert consensus reached in five areas. Clinical treatments have been trialed, and diagnosis and treatment methods and medicines that have proven clinically effective have been rolled out at a faster pace. Biosecurity has been strengthened at laboratories, as has the management of blood samples for Covid-19 testing and biological samples for laboratory testing.
运用大数据、人工智能等新技术开展防控。充分利用大数据、人工智能等新技术,进行疫情趋势研判,开展流行病学调查,努力找到每一个感染者、穷尽式地追踪密切接触者并进行隔离。建立数据库,依法开展疫情防控风险数据服务,对不同风险人群进行精准识别,预判不同地区疫情风险,为促进人员有序流动和复工复产提供服务。通过5G视频实时对话平台,偏远山区的流行病学调查团队可以与几千公里之外的高级别专家实时互动交流。经公民个人授权,推广个人“健康码”“通信大数据行程卡”作为出行、复工复产复学、日常生活及出入公共场所的凭证,根据查询结果进行管控通行和分类处置,实现分区分级的精准识别、精准施策和精准防控。利用大数据技术绘制“疫情地图”,通过社区名称、地址和位置,标明疫情传播具体地点、距离、人数等,为公众防范传染提供方便。
Big data and artificial intelligence have been used in epidemic control.China has fully utilized big data, artificial intelligence, and other new technologies in research and analysis to forecast the trend of Covid-19 developments. These tools have also been exhaustively applied in epidemiological investigations to find every infected person and track every close contact for quarantine. A database has been set up in accordance with the law to provide data services for virus risk control, precisely identify different groups at risk, predict risk factors in different areas, and facilitate the orderly flow of people and the resumption of business operations. Via online platforms based on 5G technology, epidemiological teams in remote mountainous areas have been able to engage in real-time discussion with top experts thousands of miles away. With authorization from the public, health QR codes and digital travel records have been employed as permits for making trips, going to school or work, and accessing certain public venues, and for other daily errands. The results shown on the codes and records provide a base for travel control and differentiated response measures, which has made risk identification and targeted control possible in different areas and at different levels. Applying big data technology, an “epidemic map” has been created to display the specific names and locations of the communities where cases have been reported and the number of infections that has been ascertained. The map has made it easier for the public to guard against infection.
此次新冠肺炎疫情防控,为应对重大突发公共卫生事件积累了宝贵经验,同时也暴露出国家公共卫生应急管理体系存在的不足。中国将认真总结疫情防控和医疗救治经验教训,研究采取一系列重要举措,补短板、强弱项。改革完善疾病预防控制体系,建设平战结合的重大疫情防控救治体系,健全应急物资保障体系,加强构建关键核心技术攻关新型举国体制,深入开展爱国卫生运动,不断完善公共卫生体系,切实提高应对突发重大公共卫生事件的能力和水平,更好维护人民生命安全和身体健康。
Through the battle against Covid-19, China has accumulated valuable experience in responding to major public health emergencies, and deficiencies in the national response system have been exposed. Summarizing this experience and learning from lessons, China will adopt a series of important measures to reinforce weak links. China will:
• reform and improve the disease prevention and control system;
• establish a major epidemic prevention, control and treatment system adapted to both times of peace and times of crisis;
• improve the emergency supply system;
• strengthen the new strategy of pooling nationwide resources for breakthroughs in core technologies;
• continue to implement initiatives to improve public sanitation; and
• improve the public health system.
China will make solid efforts to build capacity and improve its response to major public health emergencies, and better safeguard people’s lives and health.
三、凝聚抗击疫情的强大力量
III. Assembling a Powerful Force to Beat the Virus
面对未知病毒突然袭击,中国坚持人民至上、生命至上,举全国之力,快速有效调动全国资源和力量,不惜一切代价维护人民生命安全和身体健康。中国共产党以人民为中心的执政理念,中国集中力量办大事的制度特点,改革开放40多年来特别是中共十八大以来积累的雄厚综合国力和国家治理现代化建设的显著成效,中华民族同舟共济、守望相助的文化底色,中国人民深厚的家国情怀、天下情怀,汇聚成抗击疫情的强大合力。
Facing the sudden onslaught of a previously unknown virus, China has put the people’s interests first – nothing is more precious than people’s lives. It has rapidly mobilized the manpower and resources of the whole nation and done everything possible to protect the lives and health of its people. A powerful synergy has been formed thanks to the following factors: observing the people-centered governance philosophy of the CPC; China’s ability to mobilize resources to accomplish major initiatives; its composite national strength built up during more than four decades of reform and opening up, particularly since the 18th CPC National Congress held in November 2012; remarkable achievements in modernizing governance; two defining values of Chinese culture – solidarity and mutual assistance; and the profound love of the Chinese people for their family and their country.
(一)人的生命高于一切
1.Lives Are Precious
在新冠肺炎疫情突袭,人民生命安全和身体健康受到严重威胁的重大时刻,中国共产党和中国政府始终以对人民负责、对生命负责的鲜明态度,准确分析和把握形势,既多方考量、慎之又慎,又及时出手、坚决果敢,以非常之举应对非常之事,全力保障人民生命权、健康权。
At a critical time when people’s lives and health were endangered, the CPC and the Chinese government acted with a keen sense of responsibility and swiftly identified the problem. The central authorities took multiple factors into consideration, made timely and resolute decisions, employed extraordinary measures to deal with an extraordinary emergency, and made every effort to safeguard people’s lives and health.
在人民生命和经济利益之间果断抉择生命至上。疫情暴发后,以宁可一段时间内经济下滑甚至短期“停摆”,也要对人民生命安全和身体健康负责的巨大勇气,对湖北省和武汉市果断采取史无前例的全面严格管控措施。同时,在全国范围内严控人员流动,延长春节假期,停止人员聚集性活动,决定全国企业和学校延期开工开学,迅速遏制疫情的传播蔓延,避免更多人受到感染。英国《柳叶刀》社论认为,“中国的成功也伴随着巨大的社会和经济代价,中国必须做出艰难的决定,从而在国民健康与经济保护之间获得最佳平衡”。(注3)在疫情防控的关键阶段,准确把握疫情形势变化,作出统筹推进疫情防控和经济社会发展的重大决策,有序恢复生产生活秩序,推动落实分区分级精准复工复产,最大限度保障民生和人民正常生产生活。随着本土疫情防控取得重大战略成果,及时采取“外防输入、内防反弹”的防控策略,坚决防止来之不易的持续向好形势发生逆转,坚决防止人民生命安全再次面临病毒威胁。
Placing people’s lives above economic growth. When the novel coronavirus struck, China decided that it would protect the lives and health of its people even at the cost of a short-term economic downturn and even a temporary shutdown. The government took strict and comprehensive control measures, never tried before, in the city of Wuhan and Hubei Province. To stem the spread of the virus, the movement of people across the country was tightly restricted, the Chinese New Year holiday was extended, gatherings were stopped, and the spring semester and business operations were postponed. In an editorial, The Lancet stated: “China’s success has come with huge social and economic costs, and China must make difficult decisions to achieve an optimal balance between health and economic protection.”3 At the critical juncture of the fight against the virus, based on a precise understanding of the evolving situation, China took the major decision to continue Covid-19 prevention and control while resuming economic and social development. While restarting normal work in an orderly manner, it took targeted measures in different regions based on local conditions, so as to ensure people’s daily life and wellbeing to the greatest possible extent. Having succeeded in containing the spread of the virus on the mainland, the Chinese government adopted a strategy of preventing inbound infections and domestic resurgence, to ensure its hard-won progress would not be lost.
不惜一切代价抢救生命。疫情初期,病毒感染者急剧增多,中国把提高治愈率、降低病亡率作为首要任务,快速充实医疗救治力量,把优质资源集中到救治一线。采取积极、科学、灵活的救治策略,慎终如始、全力以赴救治每一位患者,从出生仅30个小时的婴儿至100多岁的老人,不计代价抢救每一位患者的生命。为了抢救病患,医务人员冒着被感染的风险采集病毒样本,没有人畏难退缩。为满足重症患者救治需要,想尽一切办法筹措人工膜肺(ECMO)设备,能买尽买,能调尽调。武汉市重症定点医院累计收治重症病例9600多例,转归为治愈的占比从14%提高到89%,超过一般病毒性肺炎救治平均水平。对伴有基础性疾病的老年患者,一人一案、精准施策,只要有一丝希望绝不轻易放弃,只要有抢救需要,人员、药品、设备、经费全力保障。疫情发生以来,湖北省成功治愈3000余位80岁以上、7位百岁以上新冠肺炎患者,多位重症老年患者是从死亡线上抢救回来的。一位70岁老人身患新冠肺炎,10多名医护人员精心救护几十天,终于挽回了老人生命,治疗费用近150万元全部由国家承担。
Saving lives at all costs. In the early stage of the epidemic, as the cases of infection soared, China made raising the cure rate and lowering the fatality rate its top priority. The best doctors and nurses were rapidly dispatched to the front line of the fight against the virus. Employing proactive, science-based, and flexible ways of treatment, they did everything possible to treat each and every patient, from an infant only 30 hours old to a centenarian. The goal was to save every single patient whatever the cost. Medical workers braved the threat of infection to collect virus specimens. No one flinched, however daunting their task. To treat seriously ill patients, local governments and hospitals tried every means to acquire and reallocate ECMO equipment. Since the virus struck, hospitals in Wuhan designated for treating severe cases have treated more than 9,600 such cases. The recovery rate has risen from 14 percent to 89 percent, higher than the average rate for normal viral pneumonia. Tailored treatment was given to elderly patients with underlying medical conditions. As long as there was the slightest hope, doctors would never give up, and the need for personnel, medicines, equipment, or funds was met. To date, more than 3,000 patients over the age of 80, including 7 centenarians, have been cured, with many of them brought back to life from the verge of death. For example, a 70-year-old patient was saved thanks to intensive treatment and care by more than 10 medical workers over a period of several weeks. The cost of his treatment, nearly RMB1.5 million, was fully covered by the government.
关心关爱海外中国公民。国家时刻挂念海外中国公民的安危,敦促、支持有关国家政府采取有效措施保障当地华侨、留学生、中资机构人员等安全。派出医疗专家组、工作组,开设远程医疗服务平台,为海外中国公民提供科学专业的疫情防控指导。协调外方全力救治在国外确诊感染的中国公民,充分调动国内专家、援外医疗队等资源,积极支持配合外方开展救治。驻外使领馆尽力履行领事保护职能,通过各种渠道宣介疫情防护知识,向留学生发放100多万份“健康包”。协助在海外确有困难的中国公民有序回国。
Care and compassion for Chinese citizens overseas. China takes the safety of its citizens abroad very seriously. It has urged the governments of other countries to take effective measures to ensure the safety of Chinese students, the personnel of Chinese-funded institutions, and other Chinese nationals in their countries, and has supported them in doing so. Medical expert teams and work groups have been dispatched overseas and telemedicine service platforms set up, which provide scientific and professional guidance on Covid-19 prevention and control for Chinese citizens in other countries. Chinese medical teams have worked with host countries to ensure the best possible treatment for Chinese citizens diagnosed with infection. China has fully mobilized experts at home, medical teams on foreign aid missions, and other resources to assist foreign countries to provide treatment to these patients. Performing their consular protection duties, Chinese embassies and consulates abroad have disseminated information on Covid-19 prevention and self-protection through all channels, and have provided more than 1 million “health kits” to overseas Chinese students. They have also helped overseas Chinese citizens in difficulty to return home.
以国之名悼念逝者。4月4日清明节,中国举行全国性哀悼活动,深切悼念抗击疫情斗争牺牲烈士和逝世同胞,为没有等来春天的生命默哀,向所有用生命守护生命的英雄致敬。从最高领导人到普通民众,14亿中国人民以最深的怀念为牺牲烈士和逝世同胞送行。中国以国家之名和最高仪式祭奠逝者,是国家对人民个体尊严与生命的尊重与敬畏,是14亿中国人民集体情感背后的团结和力量。
National tribute to the deceased. On April 4, the Chinese traditional Tomb-sweeping Day, China paid tribute to all those who had given their lives in the fight against Covid-19, and those who had died of the disease. People throughout the country observed a silence to mourn the loss of lives and pay tribute to heroes who had protected others’ lives at the cost of their own. From the top leader to ordinary people, 1.4 billion Chinese bade farewell to their dear departed. This solemn national ceremony demonstrates that the country respects and holds in awe the dignity and lives of people as individuals. It signifies the solidarity and strength of 1.4 billion Chinese.
(二)举全国之力抗击疫情
2.Mobilizing the Whole Country to Fight the Epidemic
一方有难,八方支援。疫情发生后,全国上下紧急行动,依托强大综合国力,开展全方位的人力组织战、物资保障战、科技突击战、资源运动战,全力支援湖北省和武汉市抗击疫情,在最短时间集中最大力量阻断疫情传播。“中方行动速度之快、规模之大,世所罕见,展现出中国速度、中国规模、中国效率”。(注4)
When a disaster strikes in one location, help comes from all quarters. After the outbreak, the entire country acted promptly. Relying on its overall national strength, China mobilized the people, enhanced R&D, procured supplies, and brought them to those in need rapidly. It mustered the support of the whole country to assist Hubei, and particularly Wuhan, to combat the disease. It pooled all its strength in the shortest period of time, and halted the spread of the epidemic. Hailing the speed and scale of China’s response, WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus described it as unprecedented, and said it showed the efficiency and the strength of China’s system.4
开展新中国成立以来规模最大的医疗支援行动。调动全国医疗资源和力量,全力支持湖北省和武汉市医疗救治。自1月24日除夕至3月8日,全国共调集346支国家医疗队、4.26万名医务人员、900多名公共卫生人员驰援湖北。19个省份以对口支援、以省包市的方式支援湖北省除武汉市以外16个地市,各省在发生疫情、防控救治任务十分繁重的情况下,集中优质医疗资源支援湖北省和武汉市。人民解放军派出4000多名医务人员支援湖北,承担火神山医院等3家医疗机构的医疗救治任务,空军出动运输机紧急运送医疗物资。各医疗队从接受指令到组建2小时内完成,24小时内抵达,并自带7天防护物资,抵达后迅速开展救治。在全国紧急调配全自动测温仪、负压救护车、呼吸机、心电监护仪等重点医疗物资支援湖北省和武汉市(表1)。从全国调集4万名建设者和几千台机械设备,仅用10天建成有1000张病床的火神山医院,仅用12天建成有1600张病床的雷神山医院。短短10多天建成16座方舱医院,共有1.4万余张床位。加强临床血液供应,10个省份无偿支援湖北省红细胞4.5万单位,血小板1762个治疗量,新鲜冰冻血浆137万毫升(不含恢复期血浆)。大规模、强有力的医疗支援行动,有力保障了湖北省和武汉市救治,极大缓解了重灾区医疗资源严重不足的压力。
Launching the largest medical assistance operation since the founding of the PRC. China mobilized all its medical resources to support the efforts in Wuhan and other locations in Hubei. From January 24, Chinese New Year’s Eve, to March 8, it rallied 346 national medical teams, consisting of 42,600 medical workers and more than 900 public health professionals to the immediate aid of Hubei and the city of Wuhan. Nineteen provinces and equivalent administrative units assisted 16 other cities in Hubei in the form of paired assistance. While burdened with the heavy responsibility of coronavirus prevention and control and treatment of patients in their home cities, they still pooled together quality medical resources to assist Hubei and Wuhan.
The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) dispatched over 4,000 medical personnel to Hubei to work in epidemic control. They took on medical work in three designated medical institutions, including Huoshenshan Hospital in Wuhan. The PLA Air Force dispatched aircraft to transport emergency medical supplies. Medical teams were formed within two hours of receiving the order, and they arrived at their destinations within 24 hours, carrying a seven-day stock of protective materials. On arrival, they started to treat patients right away. The government urgently solicited automatic temperature measuring equipment, negative pressure ambulances, ventilators, electrocardiogram monitors, and other key medical supplies from across the country for Wuhan and other locations in Hubei (see Table 1). It mobilized 40,000 construction workers and several thousand sets of machinery and equipment to build two hospitals. The construction of the 1,000-bed Huoshenshan Hospital was completed in just 10 days, and that of the 1,600-bed Leishenshan Hospital in just 12 days. In 10 short days, 16 temporary treatment centers providing over 14,000 beds were built. To increase blood supply for clinical use in surgery, 10 provinces donated to Hubei 45,000 units of red blood cells, 1,762 therapeutic doses of platelets, and 1,370 liters of fresh frozen plasma (not including convalescent plasma). These massive and powerful medical assistance actions have guaranteed Covid-19 treatment in Hubei and Wuhan, greatly relieving the pressure on the hardest-hit areas caused by severe shortages of medical resources.
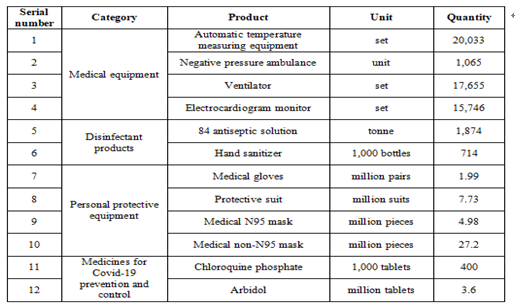
Table 1. Medical Supplies Sent to Hubei since the Onset of the Epidemic (As of April 30)
大力加强医疗物资生产供应和医疗支持服务。疫情防控阻击战,也是后勤保障战。疫情初期,武汉市医疗防护物资极度短缺,为了节省防护用品、争分夺秒抢救病患,一线医护人员克服困难,最大限度地延长防护用品使用时间。为尽快解决医疗资源短缺和病患急剧增多的突出矛盾,中国充分发挥制造业门类全、韧性强和产业链完整配套的优势,克服春节假期停工减产等不利因素,开足马力,深挖潜力,全力保障上下游原料供应和物流运输,保证疫情防控物资的大规模生产与配送。医疗企业克服工人返岗不足等困难,以最快速度恢复医疗用品生产,最大限度扩大产能。其他行业企业迅速调整转产,生产口罩、防护服、消毒液、测温仪等防疫物资,有效扩大了疫情防控物资的生产供应。快速启动防控医疗物资应急审批程序,全面加强质量安全监管,确保以最快的速度批准上市、促产保供,截至5月31日,共应急批准17个药物和疫苗的19件临床试验申请,附条件批准2个疫情防控用药上市。在各方共同努力下,医用物资产能不断提升,医用物资保供实现从“紧缺”到“紧平衡”“动态平衡”“动态足额供应”的跨越式提升(表2)。2月初,医用非N95口罩、医用N95口罩日产量分别为586万只、13万只,到4月底分别超过2亿只、500万只。畅通供应链条和物流渠道,建立联保联供协作机制,源源不断地把全国支援物资运送到疫情防控重点地区。
Increasing the production and supply of medical supplies and medical support services.Victory in the battle against Covid-19 depends on logistical support. In view of the extreme scarcity of medical protective materials in Wuhan during the early stage of the epidemic, medical workers on the front line overcame difficulties and used every item for the longest possible time, so as to conserve them in the race to save lives. To address the shortfall in medical resources while patient numbers surged, China exploited the full strength of its comprehensive and resilient manufacturing sector and its complete industrial chain. To overcome the unfavorable combination of a pause in work and the resultant decline in manufacturing output during the Chinese New Year holiday, the Chinese government mobilized factories across the country to operate at full capacity and tap into their full potential. With all its strength, it supported raw materials supplies and transport facilities throughout the industrial chain, so as to ensure large-scale production and distribution of materials for epidemic prevention and control. Medical manufacturers overcame such difficulties as labor shortages caused by workers not having returned to their posts. They resumed production as quickly as possible, and expanded capacity to the maximum. Enterprises in other industries made rapid adjustments to their manufacturing facilities and turned to producing masks, protective suits, disinfectants, temperature measuring devices, and other products for the fight against the epidemic, thereby effectively expanding the overall output of such materials and equipment. The Chinese government quickly started procedures to review applications for producing medical supplies in times of emergency, and imposed stricter quality and safety supervision across the board, so as to facilitate production, ensure the quickest approval for sale, and guarantee supplies. As of May 31, relevant authorities had approved 19 applications for clinical trials of 17 medicines and vaccines for coronavirus prevention and control, and conditionally approved the applications for sale of two medicines. Thanks to the joint efforts of many parties, manufacturing capacity for medical supplies increased steadily, and efforts to ensure the supply of medical materials and equipment achieved rapid progress: from acute shortage to borderline sufficiency, then from demand-supply balance to timely and sufficient supplies (see Table 2). The daily output of medical N95 masks and medical non-N95 masks increased from 130,000 and 5.86 million in early February to over 5 million and 200 million by the end of April. These efforts opened up unimpeded supply chains and logistics channels, gave birth to a coordination mechanism ensuring material supply, and allowed continuous transport of materials from across the country to the hardest-hit areas.
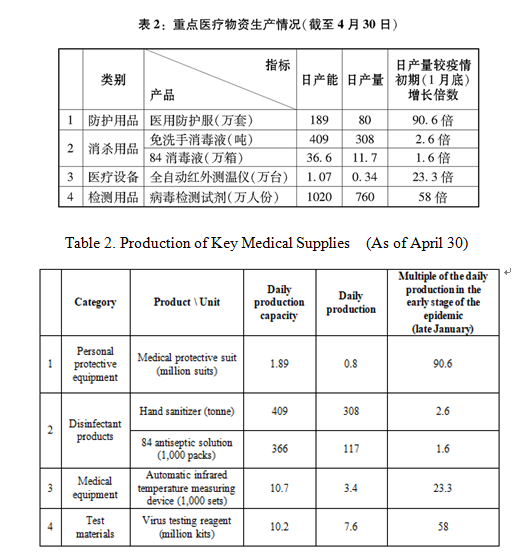
Table 2. Production of Key Medical Supplies (As of April 30)
统筹协调生活物资保障。离汉通道关闭后,武汉市近千万人居家隔离,每天需要消耗大量的粮食、蔬菜、肉蛋奶。加强联动协调,建立央地协同、政企联动的9省联保联供协作和500家应急保供企业调运机制,加大粮油供应力度,投放中央冻猪肉储备,提升蔬菜大省产品供应能力,组织紧急物资运输队伍,全力保障湖北省特别是武汉市居民生活必需品的生产、库存、供应和价格稳定。1月27日至3月19日,全国通过铁路、公路、水运、民航、邮政快递等运输方式向湖北地区运送防疫物资和生活物资92.88万吨,运送电煤、燃油等生产物资148.7万吨,煤、电、油、气、热等能源供应充足,保障了湖北省、武汉市社会正常运转和隔离措施顺利实施。武汉市将生活物资配送纳入社区服务,打通生活物资配送从商场、超市到小区的最后环节,通过无接触配送方式将经过检疫、符合防疫标准的蔬菜直送社区,保障了隔离期间居民生活需要和防疫安全。
Coordinating and ensuring the supply of daily necessities.Once outbound traffic from Wuhan had been halted, nearly 10 million people were under home isolation in the city, requiring a huge amount of grain, vegetables, meat, eggs, and milk every day. A coordination mechanism was established to ensure supply of such products, which involved nine provinces, and 500 enterprises for prioritizing the shipment of supplies in times of emergency. The mechanism involved coordination between central and local governments, and joint actions by government and enterprises. It boosted the supply of grain and cooking oil, released central government reserves of frozen pork, and raised the supply capacity of provinces which are major vegetable bases. Transport teams were organized for emergency supplies, and forceful measures were taken to ensure the production, stocks, supply, and price stability of daily necessities for residents in Hubei, and particularly in Wuhan. From January 27 to March 19, 928,800 tonnes of epidemic prevention and control materials and daily necessities were transported from across the country to Hubei via railway, highway, waterway, civil aviation, and express postal services. Bulk goods such as thermal coal and fuel totaling 1.49 million tonnes were also shipped. Sufficient supplies of coal, electricity, fuel, gas, and heat ensured the normal functioning of society and the smooth implementation of quarantine measures in Hubei and particularly in Wuhan. In Wuhan, delivery of daily necessities was included in community services, thus the last link of daily distribution – from supermarkets to communities – was assured. Through contactless delivery, vegetables that had gone through quarantine and met the standards were delivered directly to communities, meeting residents’ needs and ensuring safety in terms of epidemic prevention.
社会力量广泛参与。工会、共青团、妇联等人民团体和群众组织,组织动员所联系群众积极投身疫情防控。城乡居民、企业、社会组织等纷纷捐款捐物、献出爱心。各级慈善组织、红十字会加强捐赠资金和物资的调配和拨付,将捐赠款物重点投向湖北省和武汉市等疫情严重地区。截至5月31日,累计接受社会捐赠资金约389.3亿元、物资约9.9亿件,累计拨付捐款资金约328.3亿元、物资约9.4亿件。
Public participation in virus control. Trade unions, Communist Youth League organizations, women’s federations, and other mass organizations organized and mobilized their contacts among the general public to get involved in Covid-19 prevention and control. Urban and rural residents, enterprises, and social organizations donated money and materials. Charities and the Red Cross Society of China improved the allocation of donated funds and materials, with a focus on Wuhan and other severely affected areas inside Hubei Province and elsewhere. As of May 31, they had received donations totaling about RMB38.93 billion and 990 million items of different materials. Of these, RMB32.83 billion and 940 million items had been disbursed.
疫情发生后,港澳台同胞和海外侨胞通过各种方式和渠道伸出援手,积极捐款和捐赠各类防疫物资,体现了浓浓的同胞亲情,体现了海内外中华儿女守望相助、共克时艰的凝聚力向心力。
Since the onset of the epidemic, fellow countrymen and women in Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan, and overseas Chinese have given a helping hand through various means and channels. They have actively donated money and materials for epidemic prevention and control. This shows how much we Chinese at home and abroad are committed to each other and demonstrates the unity and cohesion of the Chinese nation in times of difficulty.
(三)平衡疫情防控与经济社会民生
3.Coordinating Prevention and Control with Social and Economic Development
在毫不放松加强疫情防控的同时,稳妥有序放开经济和社会活动,做好“六稳”工作,落实“六保”任务,形成同疫情防控相适应的经济社会运行秩序,努力将疫情对经济社会发展的冲击和影响降到最低,为抗击疫情提供有力的物资保障和社会保障。
Without compromising Covid-19 control, China has steadily resumed social and economic activities in an orderly way, so as to stabilize the six fronts (employment, finance, foreign trade, inbound investment, domestic investment, and market expectations), and guarantee the six priorities (jobs, daily living needs, food and energy, industrial and supply chains, the interests of market players, and the smooth functioning of grassroots government). It has fostered a social and economic order under the conditions imposed by Covid-19 control and striven to minimize their impact on social and economic development, thus providing a strong material and social buttress for the fight against the epidemic.
保持社会稳定、有序运转。着力加强社会安全稳定工作,加强社会治安管理,强化防疫物资质量和价格监管,维护市场秩序和社会稳定。及时出台受疫情影响困难群众兜底保障政策,有效保障基本生活。将心理危机干预纳入疫情防控,妥善处理疫情防控中思想和心理问题,加强思想引导和心理疏导,培育理性平和、积极健康的心态,及时预防化解涉疫矛盾纠纷。疫情大考下,在交通管制、全民居家隔离等严格管控措施的情况下,不论是城市还是农村,水、电、燃气、通信不停,生活物资供应不断,社会秩序不乱,食品、药品、能源、基础工业品、基本公共服务等关系国计民生的重点行业有序运转,14亿人民的基本民生得到有效保障,经济社会大局保持了稳定有序。
Maintaining social order and stability. China has made every effort to ensure social order and stability, market order, public security, and supervision over the quality and pricing of epidemic-control supplies. It has adopted timely policies to ensure the basic livelihood of people in difficulties caused by Covid-19. Psychological counseling is provided to ease distress, nurture a healthy mindset, prevent and resolve potential problems, and defuse local disputes. Despite strict measures such as traffic control and home-based quarantine, the economy and society have remained resilient. The supply of water, electricity, natural gas and telecommunication services continues, as does the supply of daily necessities in urban and rural areas. Key sectors providing food, pharmaceuticals, energy, basic industrial products, and public services that are essential to social stability and people’s wellbeing are in normal operation, meeting the basic needs of 1.4 billion people.
有序推动复工复产。密集制定出台多项政策,为企业特别是中小企业和个体工商户减负纾困,实施减费降税,增加财政补贴,加大金融支持,减负稳岗扩就业,优化政府服务。各地方及时制定实施细则,将疫情防控、公共事业运行、群众生活必需等领域的1万多家企业列为重点,通过租用专车、专列、包机等方式“点对点”“一站式”帮助农民工返岗,并从个人防护物资、人流、物流等方面为企业复工提供全方位服务。针对公共交通运输、餐饮、住宿、旅游、体育、娱乐等受疫情影响较大的行业,采取免征增值税等税收优惠政策。阶段性减免企业社保费,缓缴住房公积金,免收公路通行费,降低企业用电用气价格,减轻小微企业和个体工商户房租负担。对中小微企业贷款实施临时性延期还本付息、新增优惠利率贷款。支持大学生、农民工等重点群体创业就业,扩大中小微企业稳岗返还政策受益面,发力稳就业,促进中小企业发展。用好用足出口退税、出口信用保险政策,扩大出口信贷投放,开拓多元化市场,加快压减外资准入负面清单,持续扩大外资市场准入,为企业“补血”“减负”“拓空间”。国有企业发挥主力军作用,带动上下游产业和中小企业全面复工复产。截至4月底,全国规模以上工业企业复工率超过99%,中小微企业复工率达到88.4%,重大项目复工率超过95%;湖北全省规模以上工业企业复工率、员工到岗率分别达到98.2%、92.1%,整体接近全国平均水平。一批国家重点科技专项、超级民生工程、重大标志性外资项目重现往日繁忙景象。中国经济运行加快回归常态,经济活力正在快速释放。
Orderly resumption of work.The central government has quickly adopted a host of policies to reduce the burdens of businesses, particularly small and medium enterprises and self-employed people. These include measures such as reducing fees and lowering taxes, increasing government subsidies, strengthening financial support, stabilizing and expanding employment, and improving government services.
Local governments have issued detailed rules to implement these policies, especially to help the 10,000 plus key enterprises essential to Covid-19 control, public services, and daily necessities. Comprehensive services are being provided to help enterprises to resume operation, including providing personal protective gear and facilitating the flow of labor and materials. Point-to-point buses, trains and planes were chartered to send migrant workers back to their work posts. Preferential tax treatments such as exemption from value-added tax are available to businesses in transport, catering, hospitality, tourism, sport, entertainment and other sectors hit hard by the epidemic. Businesses also enjoy a temporary reduction in or exemption from social security contributions, a waiver of highway tolls, and reduced electricity and gas prices, and they are allowed to postpone their housing provident fund payments. Rent is being reduced for small and micro enterprises and the self-employed. The principal and interest repayment periods on loans to micro, small and medium enterprises are being extended, and more concessional loans are being provided. Key groups such as college graduates and migrant workers are receiving support in finding jobs or starting businesses. Subsidies given to micro, small and medium enterprises to reduce layoffs are being extended to more businesses so as to stabilize employment and help them survive. Policies on export tax rebates and export credit insurance are being put to good use, export credits expanded and new export markets explored. The negative list of market access for foreign investment has been cut to attract foreign investment. All these efforts will cut burdens on enterprises and stimulate their growth. State-owned enterprises have taken the lead in resuming operations, providing impetus for upstream and downstream industries, including small and medium enterprises. By the end of April, 99 percent of companies of designated size – with a revenue of more than RMB20 million per annum – had resumed operations, as had 88.4 percent of micro, small and medium enterprises. Construction of over 95 percent of major projects across the country had resumed. In Hubei Province, more than 98.2 percent of enterprises of designated size had resumed operations, and 92.1 percent of their employees had returned to their jobs, and both these figures were close to the national average. Now, work on some key national science and technology projects, major national projects related to people’s daily lives, and landmark foreign-funded projects has resumed. The Chinese economy is accelerating its return to normal operation, and it is becoming increasingly robust.
公众生活逐步恢复。随着疫情防控形势积极向好,公众日常生活逐步恢复。公共交通全面恢复运行,餐饮门店有序开放堂食。“五一”假期重新绽放活力,全国铁路、道路、水路、民航累计发送旅客1.21亿人次,全国累计接待国内游客1.15亿人次,实现国内旅游收入475.6亿元,经受住了疫情和假期的双重考验。在落实防控措施前提下,全面开放商场、超市、宾馆、餐馆等生活场所。全国分批分次复学复课,截至5月31日,各省(自治区、直辖市)和新疆生产建设兵团中小学部分学段均已开学,共有1.63亿学生(含幼儿园)返校。中国社会正在恢复往常热闹景象,人气日益回暖,消费逐步复苏。
Gradual return to normal life.With steady progress made in Covid-19 control, public life is gradually returning to normal. Public transport services have fully resumed. More restaurants are reopening to the public. The May Day holiday in China saw a bustle of activity. During the five-day holiday, 121 million trips were made via railways, highways, waterways and air; and 115 million visits were paid to domestic tourist attractions, generating revenue of RMB47.56 billion. Services such as shops, supermarkets, hotels, and restaurants have reopened their doors under Covid-19 control conditions. Students across the country have resumed their studies, and some have now returned to school. As of May 31, 163 million students and children in some grades of kindergarten, elementary and secondary schools across the country had returned to school or kindergarten. Public life is returning to normal in China, with people resuming their daily routines and consumption gradually picking up.
(四)14亿中国人民坚韧奉献守望相助
4.Uniting as One – China’s Billion People
国家兴亡,匹夫有责。14亿中国人民,不分男女老幼,不论岗位分工,都自觉投入抗击疫情的人民战争,坚韧团结、和衷共济,凝聚起抗击疫情的磅礴力量。14亿中国人民都是抗击疫情的伟大战士。
All citizens share a responsibility for the fate of their country. The 1.4 billion Chinese people, irrespective of their gender, age, and occupation, have plunged themselves into the battle against the epidemic. Resilient and united, they represent a formidable force.
医务工作者白衣执甲、逆行出征。从年逾古稀的院士专家,到90后、00后的年轻医护人员,面对疫情义无反顾、坚定前行。54万名湖北省和武汉市医务人员冲锋在前,4万多名军地医务人员第一时间驰援湖北省和武汉市,数百万名医务人员战斗在全国抗疫一线。他们以对人民的赤诚和对生命的敬佑,争分夺秒、舍生忘死、连续作战,挽救了一个又一个垂危生命,用血肉之躯构筑起阻击病毒的钢铁长城,为病毒肆虐的漫漫黑夜带来了光明,守护了国家和民族生生不息的希望。他们与病毒直面战斗,承受难以想象的身体和心理压力,付出巨大牺牲,2000多人确诊感染,几十人以身殉职。没有人生而英勇,只是选择了无畏。中国医生的医者仁心和大爱无疆,永远铭刻在中华民族历史上,永远铭刻在中国人民心中。
Medical workers rose to the challenge. Medical workers, from the very young to the very old, showed no hesitation in confronting the epidemic. At the outset, some 540,000 medical workers from Wuhan and other parts of Hubei plunged into the fray, joined soon by more than 40,000 civilian and military medical workers who rushed from other parts of the country. Millions of medical workers grappled with the epidemic at the front line across the country. Showing professional devotion and a deep respect for life, many of them risked their own lives, racing against time and working round the clock to try to save every patient. They built a Great Wall against the virus, bringing light and hope to the nation at a dark time. They endured tremendous fatigue and stress, and paid a heavy price. More than 2,000 medical workers were infected, and scores died in the line of duty. No one is born a hero, yet their selflessness made them fearless. These people, with the nobility, kindness, and devotion that are intrinsic to their profession, have etched an unforgettable chapter in the history of the Chinese nation and in the hearts of the Chinese people.
武汉人民和湖北人民顾全大局、顽强不屈,为阻击病毒作出巨大牺牲。武汉人民、湖北人民面对离汉离鄂通道关闭后与外隔绝、交通停滞、城市“停摆”,克服了近距离接触病毒、医疗资源和生活物资紧张以及长时间隔离带来的困难,忍住失去至爱亲朋的痛苦,服从大局,咬紧牙关,团结坚守。在伟大的抗疫战争中,英雄的武汉人民、湖北人民将载入史册为人们所铭记。
People in Wuhan and other parts of Hubei fought with resolve against the novel coronavirus and made sacrifices to contain its spread. The people of Wuhan and Hubei were confronted with many challenges. All channels of exit from the city and the province were temporarily closed, intra-city public transport was suspended, and the capital city came to a standstill. The high risk of infection, tight supply of medical and daily necessities, and extended period of isolation were compounded by the trauma of bereavement for those who lost friends or family members to the virus. However, with grit in their hearts and the wider interests of others in their minds, they united to stop the transmission of the virus. In this great war, their heroism will be remembered and will go down in history.
社区工作者、公安民警、海关关员、基层干部、下沉干部不辞辛苦、日夜值守,为保护人民生命安全牺牲奉献。400万名社区工作者奋战在全国65万个城乡社区中,监测疫情、测量体温、排查人员、站岗值守、宣传政策、防疫消杀,认真细致,尽职尽责,守好疫情防控“第一关口”。公安民警及辅警驻守医院、转运病人、街道巡逻、维护秩序,面对急难险重任务勇挑重担,130多人牺牲在工作岗位。海关关员依法履行卫生检疫职责,筑牢口岸检疫防线。社区防控一线广大党员、干部及时将党和政府的声音传导到基层,组织动员群众做好防控,积极为群众排忧解难,抓实抓细网格服务管理。
Community workers, primary and community-level officials, officials sent to work in communities, police, and customs officers worked day and night to protect lives and public safety. Some 4 million community workers are working in around 650,000 urban and rural communities, monitoring the situation, taking body temperatures, screening for infection, disseminating government policies, and sanitizing neighborhoods. Dedicated and responsible, they have meticulously protected their communities from the virus. CPC members working in communities quickly communicated the policies of the Party and the government, mobilized residents to engage in epidemic prevention and control, and actively helped them solve their daily difficulties. They divided communities into sub-units called grids to improve services and management. Police and auxiliary police officers handled emergent, dangerous, difficult, and burdensome tasks such as guarding hospitals, transporting patients, and patrolling the streets to maintain order. More than 130 have died in the line of duty. Customs officers have applied the law and carried out quarantine and other health-related duties, preventing the virus from entering the country.
快递小哥、环卫工人、道路运输从业人员、新闻工作者、志愿者等各行各业工作者不惧风雨、敬业坚守。疫情期间,千家万户关门闭户,数百万快递员顶风冒雪、冒疫前行,在城市乡村奔波,给人们送来温暖。全国180万环卫工人起早贪黑、不辞辛劳,高标准做好卫生清扫、消毒杀菌、医疗废物集中处理、垃圾清理清运。数千万道路运输从业人员坚守岗位,许多城市出租车司机没有停工,有力保障疫情防控、生产生活物资运输和复工复产。新闻工作者不惧风险、深入一线,记录中国抗疫的点点滴滴,传递中国人民抗击疫情的温情和力量。许多普通人投入一线志愿服务,社区值守、排查患者、清洁消杀、买药送菜,缓解居民燃眉之急。据不完全统计,截至5月31日,全国参与疫情防控的注册志愿者达到881万人,志愿服务项目超过46万个,记录志愿服务时间超过2.9亿小时。
Couriers, sanitation workers, transport employees, media workers, volunteers, and many people from other sectors of society also devoted themselves to the fight against the epidemic. When things were at their most serious, while people kept their doors closed, millions of couriers braved the virus and the cold, delivering warmth and comfort to people in cities and rural areas. China’s 1.8 million sanitation workers worked from dawn to dusk to clean and disinfect public spaces, and collect and transport medical and other wastes to centralized treatment facilities. Tens of millions of transport employees, including taxi drivers in many cities, remained at their posts, providing a vital support to epidemic prevention and control, carrying supplies for work and daily life, and helping to get the country back to work. Some media workers also worked at the front line, recording the battle against the epidemic, spreading warmth, and evoking strength. Many ordinary people volunteered at the front line, standing guard in communities, screening for infection, carrying out cleaning and disinfection work, and buying medicines and delivering groceries for other residents’ pressing needs. Preliminary statistics show that as of May 31, 8.81 million registered volunteers across the country had participated in more than 460,000 volunteer projects, rendering a total of more than 290 million hours of voluntary service.
广大民众扛起责任、众志成城,自觉参与抗击疫情。危难面前,中国人民对中国共产党和中国政府高度信任,勇敢承担起社会责任,为取得抗疫胜利约束自我乃至牺牲自我。疫情暴发正值春节假期,国家一声令下,全民响应,一致行动,整个社会紧急停下脚步。人们取消了春节期间的走亲访友和各种聚会,克服困难就地隔离,外出自觉佩戴口罩、测量体温、保持社交距离。保护自己就是保护别人、就是为国家作贡献成为社会共识和每个人的自觉行动。人们长时间在家隔离,上网课、学美食、陪家人,用各种方式缓解压力,以积极乐观的态度抗击疫情。“所有好的做法如果想要奏效,必须要有公众的集体意愿。正因如此,中国有能力通过传统公共卫生干预方法应对一种新型的未知病毒”(注5)。
The general public shouldered their responsibilities, united as one, and proactively participated in epidemic prevention and control. In the face of adversity, Chinese people have great faith in the Party and the government. They courageously shouldered their social responsibilities, and on this occasion made great sacrifices to win the battle against the epidemic. The Chinese New Year holiday arrived amid the epidemic. Following government orders to contain the virus, the whole population acted in concert, and social exchanges shrank to a minimum. Visits to friends and relatives were canceled and so were other gatherings; people quarantined themselves, wore masks, began to take their body temperature regularly, and practiced other social distancing measures. The consensus was that protecting oneself was protecting others and making contribution to the country, so everyone took voluntary actions against the virus. People stayed at home for extended periods of time, taking online courses, honing culinary skills, and spending time with their families. Many found creative ways to keep themselves occupied, and confronted the epidemic with a positive attitude. Speaking of the general public in China, Dr. Bruce Aylward, former assistant director general of the WHO and senior advisor to WHO director general, said at the press conference of WHO-China Joint Mission on Covid-19 held on February 24 in Beijing, “And that’s because we want to emphasize this can’t work without the collective will of the population contributing to it. And that’s what really distinguishes this country, this response and the ability to take these old-fashioned strategies, some of the earliest ones we had in public health, apply them to the most modern virus and somehow do that.”5
重大危机是考验执政党执政理念、执政效能的试金石。中国在较短时间内遏制疫情蔓延,根本在于中国共产党的坚强领导。中国共产党有坚强有力的领导核心,有以人民为中心的执政理念,面对疫情危机,迅速科学作出决策,实行高效有力的危机应对。中国共产党严密的组织体系和高效的运行机制,在短时间内建立横向到边、纵向到底的危机应对机制,有效调动各方积极性,全国上下令行禁止、统一行动。中国共产党460多万个基层组织,广泛动员群众、组织群众、凝聚群众、服务群众,筑起一座座抗击疫情的坚强堡垒。在疫情危及人民生命安全的危难关头,共产党员冲在最前面,全国3900多万名党员、干部战斗在抗疫一线,1300多万名党员参加志愿服务,近400名党员、干部为保卫人民生命安全献出了宝贵生命。广大党员自觉捐款,为疫情防控斗争真情奉献。注重在疫情考验中锤炼党员干部,检验为民初心和责任担当,对湖北省委和武汉市委领导班子作出调整补充,对不担当、不作为、失职渎职的党员干部严肃问责,对敢于担当、认真负责的党员干部大力褒奖、大胆使用,立起了鲜明导向。历经疫情磨砺,中国人民更加深切地认识到,风雨来袭,中国共产党的领导是最重要的保障、最可靠的依托,对中国共产党更加拥护和信赖,对中国制度更加充满信心。
A major crisis is a litmus test of the ruling Party’s governance philosophy and effectiveness. The strong leadership of the CPC has been fundamental to China’s rapid containment of the virus. The CPC has a strong leadership core, a people-oriented governance philosophy, and well-established organization and operation mechanisms. It quickly made the right decisions in response to the crisis. Under its leadership, efficient and powerful response measures were implemented. Within a short time, across-the-board crisis-response mechanisms were established down to the community level, motivating all those involved across the country to follow instructions and act as one. The CPC has more than 4.6 million primary-level organizations, which have served as strongholds against the epidemic, rallying and serving the general public. With the epidemic putting people’s lives and safety in danger, CPC members have acted as the vanguard. More than 39 million CPC members fought the virus at the front line, and more than 13 million CPC members volunteered their services. Nearly 400 CPC members have defended others’ lives and safety at the cost of their own. Party members have also voluntarily donated money for epidemic prevention and control. The CPC attaches great importance to tempering its members in times of trial, to gauge their commitment to serving the people and their sense of responsibility. The leadership of Wuhan City and Hubei Province was reshuffled, with some officials sanctioned for irresponsibility and dereliction of duty while others have been honored and promoted for their dedication and sense of responsibility. After weathering the epidemic, the Chinese people have keenly realized that the CPC leadership is the most reliable shelter against storms. Their trust in and support for the Party have increased, along with their confidence in China’s political system.
四、共同构建人类卫生健康共同体
IV. Building a Global Community of Health for All
当前,新冠肺炎疫情仍在全球肆虐,每天都有许多生命逝去。面对严重危机,人类又一次站在了何去何从的十字路口。坚持科学理性还是制造政治分歧?加强团结合作还是寻求脱钩孤立?推进多边协调还是奉行单边主义?迫切需要各个国家作出回答。中国主张,各国应为全人类前途命运和子孙后代福祉作出正确选择,秉持人类命运共同体理念,齐心协力、守望相助、携手应对,坚决遏制疫情蔓延势头,打赢疫情防控全球阻击战,护佑世界和人民康宁。
Coronavirus is raging all over the world, and lives are being lost every day. In the face of this serious crisis humanity once again stands at a crossroads. Which route shall we take? Shall we uphold science and rationality, or shall we manufacture political disputes? Strengthen unity and cooperation, or seek isolation? Promote multilateral coordination, or pursue unilateralism? Every country has a choice to make. China believes that all countries should make the choice that is right for the interests of all humanity and the wellbeing of our future generations. Upholding the vision of a global community of shared future, we should support each other and join hands to contain the spread of the virus, and protect the health and wellbeing of people across the globe.
(一)中国感谢和铭记国际社会宝贵支持和帮助
1.China Appreciates Support from the International Community
在中国疫情防控形势最艰难的时候,国际社会给予了中国和中国人民宝贵的支持和帮助。全球170多个国家领导人、50个国际和地区组织负责人以及300多个外国政党和政治组织向中国领导人来函致电、发表声明表示慰问支持。77个国家和12个国际组织为中国人民抗疫斗争提供捐赠,包括医用口罩、防护服、护目镜、呼吸机等急用医疗物资和设备。84个国家的地方政府、企业、民间机构、人士向中国提供了物资捐赠。金砖国家新开发银行、亚洲基础设施投资银行分别向中国提供70亿、24.85亿元人民币的紧急贷款,世界银行、亚洲开发银行向中国提供国家公共卫生应急管理体系建设等贷款支持。中国感谢国际社会给予的宝贵理解和支持,中国人民永远铭记在心。中华民族是懂得感恩、投桃报李的民族,中国始终在力所能及的范围内为国际社会抗击疫情提供支持。
At the time when the situation in China was at its most difficult, the international community provided valuable support and assistance to our country and our people. Leaders of more than 170 countries, heads of 50 international and regional organizations, and more than 300 foreign political parties and organizations expressed solidarity and support for China through phone calls, letters, and statements. Seventy-seven countries and 12 international organizations donated emergency medical supplies, including masks, protective suits, goggles, and ventilators. Donations of materials were also made by local governments, enterprises, non-governmental organizations and people from 84 countries. The BRICS New Development Bank and the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank provided emergency loans of RMB7 billion and RMB2.485 billion, while the World Bank and the Asian Development Bank offered loans for the building of China’s public health emergency management system. China appreciates the understanding and support of the international community, which our people will always cherish. The Chinese nation never forgets the help and generosity it receives, and always reciprocates with the same goodwill. We are now doing all we can to support the international community in the fight against the coronavirus.
(二)中国积极开展国际交流合作
2.China Conducts Active International Exchanges and Cooperation
疫情发生以来,中国始终同国际社会开展交流合作,加强高层沟通,分享疫情信息,开展科研合作,力所能及为国际组织和其他国家提供援助,为全球抗疫贡献中国智慧、中国力量。中国共产党同110多个国家的240个政党发出共同呼吁,呼吁各方以人类安全健康为重,秉持人类命运共同体理念,携手加强国际抗疫合作。
China has been carrying out exchanges and cooperation with the international community from the outset. It has strengthened high-level communication, shared information, and cooperated in scientific research with international organizations and other countries, and done all it can to provide assistance, contributing ingenuity and strength to the global fight against the coronavirus. The CPC has issued a joint appeal with 240 political parties in more than 110 countries, calling on all stakeholders to put people’s lives and health first, uphold the vision of a global community of shared future, and pull together to combat the virus.
习近平主席亲自推动开展国际合作。疫情发生以来,习近平主席同近50位外国领导人和国际组织负责人通话或见面,介绍中国抗疫努力和成效,阐明中国始终本着公开、透明、负责任的态度,及时发布疫情信息,分享防控和救治经验,阐明中国对其他国家遭受的疫情和困难感同身受,积极提供力所能及的帮助,呼吁各方树立人类命运共同体意识,加强双多边合作,支持国际组织发挥作用,携手应对疫情挑战。习近平主席出席二十国集团领导人特别峰会并发表讲话,介绍中国抗疫经验,提出坚决打好新冠肺炎疫情防控全球阻击战、有效开展国际联防联控、积极支持国际组织发挥作用、加强国际宏观经济政策协调等4点主张和系列合作倡议,呼吁国际社会直面挑战、迅速行动。5月18日,习近平主席在第73届世界卫生大会视频会议开幕式上发表致辞,呼吁各国团结合作战胜疫情,共同构建人类卫生健康共同体,提出全力搞好疫情防控、发挥世界卫生组织作用、加大对非洲国家支持、加强全球公共卫生治理、恢复经济社会发展、加强国际合作等6点建议,并宣布两年内提供20亿美元国际援助、与联合国合作在华设立全球人道主义应急仓库和枢纽、建立30个中非对口医院合作机制、中国新冠疫苗研发完成并投入使用后将作为全球公共产品、同二十国集团成员一道落实“暂缓最贫困国家债务偿付倡议”等中国支持全球抗疫的一系列重大举措。
President Xi has personally promoted international cooperation. In phone calls or meetings with nearly 50 foreign leaders and heads of international organizations, President Xi explained China’s tactics and achievements in fighting the virus, and emphasized China’s open, transparent and responsible approach towards releasing information and sharing its experience in virus control and the treatment of infected cases. He expressed empathy for the difficulties faced by other countries, saying that China would do all it can to help them. He called on all parties to build a global community of shared future, strengthen bilateral and multilateral cooperation, and support international organizations in order to work together to meet the challenge.
President Xi delivered a speech at the G20 Extraordinary Leaders’ Summit on Covid-19 on China’s experience. In a call on the international community to rise to the challenge and act swiftly, he put forward a series of cooperation initiatives and four key proposals – launch an all-out global war against Covid-19, establish a collective response for control and treatment at the international level, support international organizations in playing their roles, and strengthen coordination of international macroeconomic policies. On May 18, he addressed the opening of the 73rd World Health Assembly, calling for a joint effort on the part of all countries to overcome the virus and build a global community of health for all. Six proposals were put forward: to do everything we can for Covid-19 control and treatment, to support the WHO in leading the global response, to provide greater support for Africa, to strengthen global governance in public health, to restore economic and social development, and to strengthen international cooperation. He also announced a series of major measures that China would take in supporting the global fight, including US$2 billion of international aid over two years, the establishment of a global humanitarian response depot and hub in China in cooperation with the United Nations, the establishment of a cooperation mechanism for Chinese hospitals to pair up with 30 African hospitals, the Covid-19 vaccine to be used as a global public product once it is developed and deployed in China, and the implementation of the Debt Service Suspension Initiative for the poorest countries together with other G20 members.
同国际社会分享疫情信息和抗疫经验。中国及时向国际社会通报疫情信息,交流防控经验,为全球防疫提供了基础性支持。疫情发生后,中国第一时间向世界卫生组织、有关国家和地区组织主动通报疫情信息,分享新冠病毒全基因组序列信息和新冠病毒核酸检测引物探针序列信息,定期向世界卫生组织和有关国家通报疫情信息。中国与东盟、欧盟、非盟、亚太经合组织、加共体、上海合作组织等国际和地区组织,以及韩国、日本、俄罗斯、美国、德国等国家,开展70多次疫情防控交流活动。国家卫生健康委汇编诊疗和防控方案并翻译成3个语种,分享给全球180多个国家、10多个国际和地区组织参照使用,并与世界卫生组织联合举办“新冠肺炎防治中国经验国际通报会”。国务院新闻办公室在武汉举行两场英文专题发布会,邀请相关专家和一线医护人员介绍中国抗疫经验和做法。中国媒体开设“全球疫情会诊室”“全球抗疫中国方案”等栏目,为各国开展交流搭建平台。中国智库和专家通过多种方式开展对外交流。中国-世界卫生组织联合专家考察组实地考察调研北京、成都、广州、深圳和武汉等地一线疫情防控工作,高度评价中国抗疫的努力和成效。
China has shared information and experience with the international community. China has provided support for global virus prevention and control by promptly sharing information and experience with the international community. It wasted no time in releasing information such as the whole coronavirus genome sequence and the specific primers and probes for detecting the coronavirus to the WHO and other relevant countries and regional organizations, and has kept them informed with regular updates. China has conducted more than 70 exchanges with international and regional organizations including ASEAN, the European Union, the African Union (AU), APEC, the Caribbean Community, and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), as well as the ROK, Japan, Russia, the United States, Germany, and other countries. The National Health Commission (NHC) has worked out diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control solutions, had them translated into three languages, and shared them with over 180 countries and more than 10 international and regional organizations. Together with the WHO it held an international briefing via video link on China’s experience in Covid-19 control. The Information Office of the State Council held two special English-language press conferences in Wuhan, inviting experts and frontline health workers to talk about China’s experience and practices. To build platforms for exchanges between countries, the Chinese media has designed a TV program Covid-19 Frontline and a newspaper column Fighting Covid-19 the Chinese Way, among others. Chinese think tanks and experts have communicated with their counterparts around the world in a variety of ways. The WHO-China Joint Mission on Covid-19 made site visits to Beijing, Chengdu, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Wuhan, and spoke highly of China’s efforts and success in prevention and control.
向国际社会提供人道主义援助。在自身疫情防控仍然面临巨大压力的情况下,中国迅速展开行动,力所能及地为国际社会提供援助。向世界卫生组织提供两批共5000万美元现汇援助,积极协助世界卫生组织在华采购个人防护用品和建立物资储备库,积极协助世界卫生组织“团结应对基金”在中国筹资,参与世界卫生组织发起的“全球合作加速开发、生产、公平获取新冠肺炎防控新工具”倡议。积极开展对外医疗援助,截至5月31日,中国共向27个国家派出29支医疗专家组,已经或正在向150个国家和4个国际组织提供抗疫援助;指导长期派驻在56个国家的援外医疗队协助驻在国开展疫情防控工作,向驻在国民众和华侨华人提供技术咨询和健康教育,举办线上线下培训400余场;地方政府、企业和民间机构、个人通过各种渠道,向150多个国家、地区和国际组织捐赠抗疫物资。中国政府始终关心在华外国人士的生命安全和身体健康,对于感染新冠肺炎的外国人士一视同仁及时进行救治。
China has provided humanitarian assistance to the international community. Even while under the tremendous pressure of coronavirus control, China has moved quickly to provide as much assistance to the international community as it can. It has provided two batches of cash support totaling US$50 million to the WHO, assisted the organization in purchasing personal protective equipment and establishing reserve centers of supplies in China, and helped its Covid-19 Solidarity Response Fund to raise funds in China. It has also participated in the WHO’s “Access to Covid-19 Tools (act) Accelerator” initiative, aiming to speed up the development, production and equitable distribution of new tools. China has been active in providing medical aid to other countries. As of May 31, China had sent 29 medical expert teams to 27 countries, and offered assistance to 150 countries and 4 international organizations. It has instructed its medical teams stationed in 56 countries to support the local fight, and provide counseling and health information to local people and overseas Chinese. They have so far organized over 400 online and offline training sessions in this regard. Local governments, enterprises, non-governmental organizations and individuals in China have donated materials to more than 150 countries and regions, and international organizations through various channels. The Chinese government has always had at heart the lives and health of foreigners in China, and it has provided undifferentiated and timely treatment to those infected with the disease.
有序开展防疫物资出口。中国在满足国内疫情防控需要的基础上,想方设法为各国采购防疫物资提供力所能及的支持和便利,打通需求对接、货源组织、物流运输、出口通关等方面堵点,畅通出口环节,有序开展防疫物资出口。采取有力措施严控质量、规范秩序,发布防疫用品国外市场准入信息指南,加强防疫物资市场和出口质量监管,保质保量向国际社会提供抗击疫情急需的防疫物资。3月1日至5月31日,中国向200个国家和地区出口防疫物资,其中,口罩706亿只,防护服3.4亿套,护目镜1.15亿个,呼吸机9.67万台,检测试剂盒2.25亿人份,红外线测温仪4029万台,出口规模呈明显增长态势,有力支持了相关国家疫情防控。1月至4月,中欧班列开行数量和发送货物量同比分别增长24%和27%,累计运送抗疫物资66万件,为维持国际产业链和供应链畅通、保障抗疫物资运输发挥了重要作用。
China has made arrangements for orderly exports of protective materials. While ensuring domestic needs, China has tried every possible means to provide support to all countries in purchasing protective materials. It has smoothed the channels for supply-demand docking, organized logistics, transport, and the supply of goods, and accelerated export customs clearance. It has taken effective measures to control product quality, regulate export procedures, issue guidelines on foreign market access, and strengthen market and export quality supervision, so as to provide other countries with goods of the highest quality. From March 1 to May 31, China exported protective materials to 200 countries and regions, among which there were more than 70.6 billion masks, 340 million protective suits, 115 million pairs of goggles, 96,700 ventilators, 225 million test kits, and 40.29 million infrared thermometers. China’s growing exports provide strong support for the prevention and control efforts of affected countries. From January to April, the number of China-Europe freight trains and the volume of goods delivered increased by 24 percent and 27 percent compared with the same period last year, and a total of 660,000 packages were transported. This has played an important role in maintaining a smooth flow of international industrial and supply chains, and in ensuring the delivery of protective supplies to relevant countries.
开展国际科研交流合作。加强同世界卫生组织沟通交流,同有关国家在溯源、药物、疫苗、检测等方面开展科研交流与合作,共享科研数据信息,共同研究防控和救治策略。科技部、国家卫生健康委、中国科协、中华医学会联合搭建“新型冠状病毒肺炎科研成果学术交流平台”,供全球科研人员发布成果、参与研讨,截至5月31日,共上线104种期刊、970篇论文和报告。国家中医药管理局联合上合组织睦邻友好合作委员会召开“中国中西医结合专家组同上海合作组织国家医院新冠肺炎视频诊断会议”,指导世界中医药学会联合会和世界针灸学会联合会开展“中医药抗疫全球直播”“国际抗疫专家大讲堂”等活动。中国科学院发布“2019新型冠状病毒资源库”,建成“新型冠状病毒国家科技资源服务系统”“新型冠状病毒肺炎科研文献共享平台”,截至5月31日,3个平台为全球超过37万用户提供近4800万次下载、浏览和检索服务。建立国际合作专家库,同有关国家开展疫苗研发、药品研发等合作。充分发挥“一带一路”国际科学组织联盟作用,推动成员之间就新冠病毒研究和新冠肺炎治疗开展科技合作。中国医疗机构、疾控机构和科学家在《柳叶刀》《科学》《自然》《新英格兰医学杂志》等国际知名学术期刊上发表数十篇高水平论文,及时发布新冠肺炎首批患者临床特征描述、人际传播风险、方舱医院经验、药物研发进展、疫苗动物实验结果等研究成果。同有关国家、世界卫生组织以及流行病防范创新联盟(CEPI)、全球疫苗免疫联盟(GAVI)等开展科研合作,加快推进疫苗研发和药物临床试验。
China has carried out international exchanges and cooperation on scientific research. China has strengthened communication and exchanges with the WHO, conducted exchanges and cooperation with other countries on research in virus traceability, medicines, vaccines, and testing, shared scientific research data and information, and jointly studied prevention, control and treatment strategies. The Ministry of Science and Technology, the NHC, the China Association for Science and Technology, and the Chinese Medical Association have jointly put in place a Covid-19 Academic Research Communication Platform for worldwide researchers to release results and participate in discussion. By May 31, a total of 104 journals and 970 papers and reports had been posted. The National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine and the SCO Committee on Good-Neighborliness, Friendship and Cooperation held a video conference on the diagnosis and treatment of Covid-19 between a group of Chinese experts on integrating traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine, and hospitals from SCO countries. It also guided the World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies and the World Federation of Acupuncture-Moxibustion Societies in organizing such events as Expert Dialogue on Covid-19 Prevention and Control with Traditional Chinese Medicine and International Lectures on Covid-19. The Chinese Academy of Sciences has released the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Resource database, and built the Novel Coronavirus National Science and Technology Resource Service System and the Covid-19 Pneumonia Scientific Literature Sharing Platform. As of May 31, the three platforms had provided nearly 48 million download, browsing and retrieval services to more than 370,000 users worldwide. China has established an international pool of experts and has cooperated with other countries in vaccine and medicine research and development. It has encouraged the Alliance of International Science Organizations in the framework of the Belt and Road Initiative to promote cooperation among its members in Covid-19 treatment and research. Chinese scientists, medical institutions, and disease control centers have published dozens of well-researched papers in some of the world’s leading academic journals such as The Lancet, Science, Nature and The New England Journal of Medicine, releasing timely results of tests on the first patients, including the clinical characteristics of the virus, the risk of human-to-human transmission, China’s experience of temporary treatment centers, medicine research and development, and experimental results of vaccines on animals. To accelerate the development of vaccines and the clinical trials of medicines, China has also carried out cooperation in scientific research with other countries, and with such organizations as the WHO, the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness and Innovation and the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunisation.
(三)国际社会团结合作共同抗疫
3.International Solidarity and Cooperation in Fighting the Pandemic
疫情在全球传播蔓延的形势令人担忧。无论是阻击病毒的传播蔓延,还是抵御不断恶化的全球经济衰退,都需要国际社会团结合作,都需要坚持多边主义、推动构建人类命运共同体。团结合作是国际社会战胜疫情最有力武器。未来的成败取决于今天的作为。中国呼吁各国紧急行动起来,更好团结起来,全面加强合作,联合抗疫,共克时艰。
The global spread of Covid-19 is causing great concern. Both the fight to rein in the virus and the endeavor to fend off a deepening global recession call for the international community to stand in unity and engage in cooperation. They also call for multilateralism, and commitment to building a global community of shared future. Solidarity and cooperation are the most powerful weapons available to the international community in the war against the pandemic. What we do today determines how we will fare in the future. China calls on all countries to act promptly, demonstrate solidarity, strengthen cooperation on all fronts, and fight the pandemic together.
有效开展联防联控国际合作。应对疫情必须各国协同作战,建立起严密的联防联控网络。疫情发生以来,世界卫生组织秉持客观公正立场,积极履行职责,采取一系列专业、科学、有效措施,为领导和推进国际抗疫合作作出了重大贡献。中国坚定支持世界卫生组织发挥全球抗疫领导作用,呼吁国际社会加大对世界卫生组织政治支持和资金投入,调动全球资源打赢疫情阻击战。中国主张,各国在世界卫生组织的指导和协调下,采取科学合理、协同联动的防控措施,科学调配医疗力量和重要物资,在防护、隔离、检测、救治、追踪等重要领域采取有力举措,同时,加强信息共享和经验交流,开展检测方法、临床救治、疫苗药物研发国际合作,继续支持各国科学家开展病毒源头和传播途径的全球科学研究。中国呼吁,二十国集团、亚太经合组织、金砖国家、上海合作组织等多边机制加大机制内对话交流与政策协调力度,二十国集团成员切实落实二十国集团领导人特别峰会达成的共识。开展联防联控国际合作,大国的负责任、担当和主动作为至关重要。中国愿同各国包括美国加强交流合作,共同应对疫情挑战,特别是在疫苗和特效药的研发、生产和分发上开展合作,为阻断病毒传播作出应有贡献。
Conducting effective international cooperation on joint prevention and control. In responding to a pandemic, all countries must act in coordination to establish an impermeable network for joint prevention and control. Since Covid-19 struck, the WHO has diligently performed its duties, adopted an objective and impartial stance, and taken a slew of professional, science-based, and effective measures. It has made a significant contribution to the fight against the pandemic by leading and advancing global cooperation. China firmly supports the WHO in playing the leading role in this global battle, and calls on the international community to give it more political and financial support, so that we can mobilize the necessary resources worldwide to defeat this virus. China maintains that all countries should implement their response under the guidance and coordination of the WHO. This includes adopting science-based, rational, and well-coordinated prevention and control measures, appropriately allocating medical resources and key supplies, adopting effective methods in key areas such as prevention, isolation, testing, treatment and case tracing, stepping up information sharing and experience exchanges, engaging in international cooperation on the research and development of testing methods, clinical treatments, drugs and vaccines, and supporting scientists around the world in studying the origin and transmission routes of the virus. China calls on multilateral organizations, including the G20, APEC, BRICS, and SCO, to increase dialogue, exchanges and policy coordination within their respective frameworks. G20 members should act on the consensus reached at the G20 Extraordinary Leaders’ Summit on Covid-19 held in late March 2020.
In international cooperation on joint prevention and control, it is essential that major countries take the initiative, fulfill their responsibilities and do their share of the work. China is ready to strengthen exchanges and cooperation with other countries including the US to jointly tackle this pandemic, especially in the fields of research, development, production and distribution of vaccines and drugs.
合作应对疫情给世界经济带来的影响。疫情在全球传播蔓延,人员流动、跨境商贸活动受阻,金融市场剧烈震荡,全球产业链供应链受到双重打击,世界经济深度衰退不可避免,国际社会联手稳定和恢复世界经济势在必行。中国愿同各国一道,在加强疫情防控的同时,一齐应对日益上升的全球经济衰退,加强国际宏观经济政策协调,共同维护全球产业链供应链的稳定、安全与畅通。新冠肺炎疫情改变了经济全球化形态,但全球化发展大势没有改变,搞“脱钩”“筑墙”“去全球化”,既割裂全球也难以自保。中国主张,各国继续推进全球化,维护以世界贸易组织为基石的多边贸易体制,减免关税、取消壁垒、畅通贸易,使全球产业链供应链安全顺畅运行,同时,实施有力有效的财政和货币政策,加强金融监管协调,维护金融市场稳定,防止引发全球性金融危机导致世界经济陷入大规模、长周期衰退。中国将继续向国际市场供应防疫物资、原料药、生活必需品等产品,坚定不移扩大改革开放,积极扩大进口,扩大对外投资,为各国抗击疫情、稳定世界经济作出更大贡献。
Managing the pandemic’s impact on the world economy through cooperation. The global spread of the pandemic has impeded the flow of people, cross-border trade, and other economic activities, triggered fluctuations on the financial market, and delivered a blow to both the industrial and supply chains, making a severe global economic recession unavoidable. It is imperative that the international community work together to stabilize and rehabilitate the world economy. While continuing to heighten epidemic control, China is ready to join forces with other countries to address the deepening global recession, stepping up international coordination on macroeconomic policies, and jointly safeguarding the stable, secure and smooth operation of international industrial and supply chains.
Covid-19 is changing the form but not the general trend of economic globalization. Decoupling, erecting walls and deglobalization may divide the world, but will not do any good to those who themselves are engaged in these acts. China believes that the international community should proceed with globalization, safeguard the multilateral trading system based on the WTO, cut tariffs, remove barriers, facilitate the flow of trade, and keep international industrial and supply chains secure and smooth. Countries also need to implement strong and effective fiscal and monetary policies, better coordinate financial regulation to keep global financial markets stable, and thus prevent a global financial crisis that may consequently plunge the world economy into a massive, protracted recession. China will continue to supply the international market with anti-epidemic materials, pharmaceutical ingredients, daily necessities, and other supplies. At the same time, China will continue to advance reform and opening up, expand imports and outbound investment, and thereby contribute further to other countries’ fight against the virus and to a stable world economy.
向应对疫情能力薄弱的国家和地区提供帮助。亚洲、非洲和拉美地区发展中国家特别是非洲国家,公共卫生体系薄弱,难以独立应对疫情带来的严峻挑战,帮助他们提升疫情防控能力和水平是全球抗疫的重中之重。中国呼吁,联合国、世界卫生组织、国际货币基金组织、世界银行等多边机构向非洲国家提供必要的紧急援助;发达国家向发展中国家特别是非洲国家提供更多物资、技术、人力支持,在全球抗疫中担负更多责任、发挥更大作用。中国积极参与并落实二十国集团缓债倡议,已宣布77个有关发展中国家暂停债务偿还。在向50多个非洲国家和非盟交付医疗援助物资、派出7个医疗专家组的基础上,中国将进一步加大援非抗疫力度,继续向非洲国家提供力所能及的支持,援助急需医疗物资,开展医疗技术合作,派遣更多医疗专家组和工作组,帮助非洲国家提升疫情防控能力和水平。中国将向联合国人道应对计划提供支持。
Assisting weaker countries and regions. Without assistance, developing countries with weaker public health systems in Asia, Africa and Latin America – especially Africa – will struggle to handle the daunting challenges posed by this pandemic. Helping them improve their capacity and performance in epidemic prevention and control should be a top priority in the global response. China calls on multilateral organizations including the UN, the WHO, the IMF and the World Bank to provide emergency aid to African countries, and calls on developed countries to take on more responsibilities, to play a bigger role in the global battle, and to provide more material, technological and personnel support to their developing counterparts, especially those in Africa. China has actively participated in and acted upon the Debt Service Suspension Initiative of the G20. It has so far announced the suspension of debt repayments from 77 developing countries. In addition to the medical supplies sent to over 50 African countries and the AU, and the seven medical expert teams dispatched to the continent, China will offer more assistance to African countries, and continue to do all in its power to offer support. This includes sending the most urgent medical supplies, conducting cooperation on medical technologies, and dispatching more medical expert teams and task forces. China will also provide support to the Covid-19 Global Humanitarian Response Plan of the UN.
坚决反对污名化和疫情政治化。面对新冠病毒对人类生命安全和健康的严重威胁,当务之急是团结合作、战胜疫情。人类的共同敌人是病毒,而不是某个国家、某个种族。中国呼吁国际社会更加团结起来,摒弃偏见和傲慢,抵制自私自利、“甩锅”推责,反对污名化和疫情政治化,让团结、合作、担当、作为的精神引领全世界人民取得全球抗疫胜利。中国是病毒受害国,也是全球抗疫贡献国,应该得到公正对待而不是责难。中国在疫情初期就向国际社会发出清晰而明确的信息,个别国家无视这些信息耽误疫情应对和拯救生命,却反称被中国“延误”,真是“欲加之罪,何患无辞”。中国始终坚持公开、透明、负责任原则及时向国际社会公布疫情信息,无端指责中国隐瞒疫情信息和死亡病例数据,是对14亿中国人民、对被病毒夺去生命的逝者、对数百万中国医护人员的极不尊重,中国对此坚决反对。新冠病毒是人类未知的新病毒,病毒溯源是科学问题,需要科学家和医学专家进行研究,基于事实和证据得出科学结论。通过转嫁责任掩盖自身问题,既不负责任也不道德,中国绝不接受任何滥诉和索赔要求。面对疫情在全球传播蔓延,中国向国际社会提供力所能及的援助,源于中国人民的古道热肠,源于对其他国家人民遭受疫情苦难的感同身受,源于面对灾难同舟共济的人道主义精神,源于大国的责任和担当,绝非输出中国模式,更不是为谋求所谓地缘政治利益。
Firmly opposing stigmatization and politicization of the virus. In the face of a novel coronavirus that poses a worldwide threat to human lives and health, the most urgent task is to defeat it through solidarity and cooperation. The common enemy of humanity is this virus, not any particular country or any particular race. China calls on the international community to come together, abandon prejudice and arrogance, resist scapegoating and other such self-serving artifices, and stand against stigmatization and politicization of the virus. In doing so we will see that the spirit of solidarity, cooperation, responsibility and dedication leads people around the world towards victory in our fight against the pandemic. China has suffered tremendously but has contributed generously to the global efforts to combat the virus. Its efforts should be duly recognized, and it should not be criticized groundlessly. Since the early days of the outbreak China has informed the rest of the world of every development in clear and unambiguous terms. Certain countries ignored this information, and now blame China for their own failure to respond to the epidemic and protect their people’s lives. Those who are intent on maligning others will easily find a pretext. China has always acted with openness, transparency and responsibility, and informed the international community of developments of the epidemic in a timely manner. The baseless accusation that China concealed epidemic information and death figures is a calculated slur on the 1.4 billion Chinese people, including those killed by the virus, and on millions of Chinese medical workers. China categorically rejects any such accusation. The novel coronavirus is a previously unknown virus. Determining its origin is a scientific issue that requires research by scientists and doctors. The conclusion must be based on facts and evidence. It is both irresponsible and immoral to play the blame game in an attempt to cover up one’s own shortcomings. China will never accept any frivolous lawsuits or compensation claims. In the face of a virus that is spreading worldwide, China has offered help to other countries to the best of its ability. It is doing so out of the kindness of its people, the empathy they have with people of other countries suffering from the pandemic, the humanitarian spirit of helping each other amid disasters, and its sense of responsibility as a major country. China is not exporting its model, nor is it pursuing selfish geopolitical interests.
健全完善惠及全人类、高效可持续的全球公共卫生体系。人类发展史也是同病毒的斗争史。当前,全球公共卫生治理存在诸多短板,全球传染病联防联控机制远未形成,国际公共卫生资源十分匮乏,逆全球化兴起使得全球公共卫生体系更加脆弱。人类终将战胜疫情,但重大公共卫生突发事件对人类来说不会是最后一次。中国呼吁,各国以此次疫情为鉴,反思教训,化危为机,以卓越的政治远见和高度负责的精神,坚持生命至上、全球一体、平等尊重、合作互助,建立健全全球公共卫生安全长效融资机制、威胁监测预警与联合响应机制、资源储备和资源配置体系等合作机制,建设惠及全人类、高效可持续的全球公共卫生体系,筑牢保障全人类生命安全和健康的坚固防线,构建人类卫生健康共同体。中国支持在全球疫情得到控制之后,坚持客观公正原则和科学专业态度,全面评估全球应对疫情工作,总结经验,弥补不足。中国主张,为人类发展计、为子孙后代谋,各国应立即行动起来,采取断然措施,最大限度消除病毒对人类的现实和潜在威胁。中国作为负责任大国,始终秉持人类命运共同体理念,积极推进和参与卫生健康领域国际合作,认真落实习近平主席在第73届世界卫生大会视频会议开幕式上提出的6点建议和5项举措,为维护地区和世界公共卫生安全,推动构建人类卫生健康共同体作出更大贡献。
Building an efficient and sustainable global public health system for the benefit of all humanity. Human history is a history of grappling with viruses. There are multiple deficiencies in current global health governance, including the absence of an international mechanism for joint prevention and control of infectious diseases and a dire shortage of international public health resources. On top of these, the upsurge in deglobalization has rendered the global public health system even more vulnerable. Humanity will prevail over the pandemic, but it will certainly not be the last major public health emergency we will encounter. China therefore calls on the international community to draw lessons from this pandemic, reflect carefully, and turn crises into opportunities. Countries should show extraordinary political vision and a strong sense of responsibility by doing the following:
• embrace a philosophy that puts life above everything else, regards the world as a whole, and stresses equality, mutual respect, cooperation and mutual assistance;
• establish sound mechanisms for international cooperation, including a long-term financing mechanism, a monitoring, early warning and joint response mechanism for threats to public health, and a mechanism for reserving and allocating resources;
• create an efficient, sustainable global public health system for all;
• fortify defenses for the lives and health of all; and
• build a global community of health for all.
China supports efforts to make a full, objective, impartial, scientific, and professional assessment of the global response once the pandemic has been brought under control. This will enable us to learn lessons and remedy weaknesses. China proposes that countries take immediate action and adopt decisive measures to minimize both the imminent and potential threats of the virus. This is in the interest of future generations and the wellbeing of all humanity. As a responsible country, China stands for the vision of a global community of shared future, and has actively participated in and advanced international cooperation in public health. It will put into action the six proposals and five measures put forward by President Xi Jinping in his speech at the opening of the 73rd World Health Assembly, and contribute more to securing regional and international public health and building a global community of health for all.
结束语
Afterword
中华民族历经磨难,但从未被压垮过,而是愈挫愈勇,不断在磨难中成长、从磨难中奋起。面对疫情,中国人民万众一心、众志成城,取得了抗击疫情重大战略成果。中国始终同各国紧紧站在一起,休戚与共,并肩战斗。
The Chinese nation has never been driven down by adversity. The more daunting the challenge, the greater the courage it has mustered. Overcoming difficulties has helped China to grow stronger. Confronted by this virus, the Chinese people have joined together as one and united their efforts. They have succeeded in containing the spread of the virus. In this battle, China will always stand together with other countries.
当前,新冠病毒仍在全球传播蔓延,国际社会将会面对更加严峻的困难和挑战。全球疫情防控战,已经成为维护全球公共卫生安全之战、维护人类健康福祉之战、维护世界繁荣发展之战、维护国际道义良知之战,事关人类前途命运。人类唯有战而胜之,别无他路。国际社会要坚定信心,团结合作。团结就是力量,胜利一定属于全人类!
Now, when the coronavirus is still spreading and causing devastation all over the world, the international community will have to face even greater difficulties and challenges. Preventing and controlling the spread of the virus has become a fight to safeguard global public health, to secure the wellbeing of humanity, to maintain world prosperity, and to enforce morality and conscience on the international community. It is a fight that will determine the future of the human race. We have no other choice but to overcome the pandemic. The international community must find resolve and forge unity. Solidarity means strength. The world will win this battle.
新冠肺炎疫情深刻影响人类发展进程,但人们对美好生活的向往和追求没有改变,和平发展、合作共赢的历史车轮依然滚滚向前。阳光总在风雨后。全世界人民心怀希望和梦想,秉持人类命运共同体理念,目标一致、团结前行,就一定能够战胜各种困难和挑战,建设更加繁荣美好的世界。
The pandemic will have a significant impact on the development of humanity, but the people’s longing for a happy life will remain unchanged. Peace, development, and win-win cooperation will prevail. The sun will always shine again after a storm. As long as the world’s peoples can cherish hopes and dreams, can embrace the idea of a global community of shared future, and can unite in pursuit of a common goal, we will be able to overcome all our current difficulties and challenges, and build a better world for all.
(注1)世界卫生组织网站:《中国-世界卫生组织新型冠状病毒肺炎(COVID-19)联合考察报告》(Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19))。https://www.who.int/publications-detail/report-of-the-who-china-joint-mission-on-coronavirus-disease-2019-(covid-19),2020年2月28日。
(注2)《柳叶刀》:《中国持续遏制新冠肺炎疫情》(Sustaining containment of COVID-19 in China)https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)30864-3/fulltext,2020年4月18日。
(注3)《柳叶刀》:《中国持续遏制新冠肺炎疫情》(Sustaining containment of COVID-19 in China)https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)30864-3/fulltext,2020年4月18日。
(注4)谭德塞:《习近平会见世界卫生组织总干事谭德塞》,新华网,http://www.xinhuanet.com/politics/leaders/2020-01/28/c_1125508831.htm,2020年1月28日。
(注5)中国-世界卫生组织联合专家考察组新闻发布会,北京,2020年2月24日。
1. Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19), February 28, 2020.
http://www.who.int/publications-detail/report-of-the-who-china-joint-mission-on-coronavirus-disease-2019-(covid-19).
2. The Lancet: “Sustaining Containment of COVID-19 in China”, April 18, 2020.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)30864-3/fulltext.
3. The Lancet: “Sustaining containment of COVID-19 in China”, April 18, 2020.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)30864-3/fulltext.
4.“China Focus: Xi Voices Full Confidence in Winning Battle against Novel Coronavirus”, Xinhuanet.com, January 28, 2020.
http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/2020-01/28/c_138739962.htm.
5. Press Conference of WHO-China Joint Mission on Covid-19, Beijing, February 24, 2020.
https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/transcripts/joint-mission-press-conference-script-english-final.pdf?sfvrsn=51c90b9e_10.
相关文章:















